The Complete Guide
to SEO On-Page
Content Optimization
Chapter: 01 Introduction to On-Page Optimization
Introduction to On-Page Optimization
Google and Bing allow companies to buy temporary visibility in search results (Adwords, Bing Ads), selling clicks to the highest bidders in highly competitive auctions at prices that can be $30 or more for just a click. But SEO can drive those clicks and organic traffic at a much lower cost and for longer periods of time. When it comes to building a brand that lasts, improving traffic through organic search is a winning strategy.
But in order to earn that organic traffic, your website’s content needs to be optimized to show up in search results. On-page content refers to the visible content and HTML source code of every landing page on a website. Content can range from text, products, tools, forms, blog posts, ebooks, images, or videos, but it all needs to be high-value in the eyes of your users and search engines.
When you create content ask yourself these questions. Why should Google rank your landing pages? Are they comprehensive and well researched? How much effort did you put into building them? Is your target keyword even on the landing page? What’s your word count? If you want to create content that ranks, it needs to be high-quality, unique, long-form, informative, engaging, and have good information architecture that shows topical authority and depth.
Having the right content and keyword strategy will drastically determine whether your landing pages get traffic from Google. But to do on-page optimization successfully, you need to have the right tools, a foundational understanding of search metrics and ranking factors, and the time and effort it takes to make your web pages worthy of page 1!
For those who want to learn how to optimize their landing pages, this is the ultimate guide on how to strategically optimize on-page content. The larger your website, the more work and time you’ll need to dedicate, so having a dedicated team of SEO-trained content creators, or seeking out the help of an SEO agency, is key for larger and enterprise-level organizations.
Why Optimization Matters
Those webmasters who take the time to incorporate the best practices of content optimization are more likely to succeed in search. Not only is content optimization more affordable than paid search marketing, 70% of marketers see it as more effective.
The primary reason why SEO has higher ROI than PPC campaigns is that SEO provides traffic to perpetuity. PPC campaigns essentially let you rent that traffic short-term and don’t provide any long-term compounding growth benefits. When a paid search campaign ends, so do the clicks. However, earning a coveted spot in the SERPs can keep organic traffic and potential customers coming to your website for years.
Optimizing content as you create it, monitoring that content’s performance in Google Analytics, and re-optimizing as time passes, are the three major steps in implementing a successful onsite SEO strategy.
What is On-Page Content?
On-page content is made up of both the visible content and the onsite technicals of your website. This includes any content you’ve created to be viewed and used by the people who visit your site, as well as the invisible meta tags, HTML markup, and bot specific elements you’ve added to your site or site code to make your content easily parsable by bots and crawlers (Google Bot, Facebook Bot, Applebot, and hundreds of others).
- Grammar, spelling, syntax, and diction should be appropriate for audience
- Topical depth: including all related ideas and topics adjacent to the core keyword you’re optimizing for
- Long-form content: needs to explore your topic in suitable breadth and depth
- Minimal redundant or unused code
- Compression and “minification” of all static files
- Using a CDN for static asset delivery off-webserver.
- Minimize post-pageload HTML DOM modifications (like inserting forms, videos)
- No render blocking javascript
- Quick time-to-first-byte (TTFB) from your webserver
- Title tags
- Meta descriptions
- Header tags (H1, H2,H3)
- Schema.org markup and microdata
- Internal Linking
- On-page navigation like jump-links and tables of contents
- Images
- Videos
- Embedded tweets, etc.
Onsite SEO, then, are the optimizations you can make to the above components so your content ranks better in search engines. These optimizations can range from changing HTML tags and meta descriptions, to including more keywords and headings, but this eBook will provide you with guidance on the many ways you can optimize your site from the comfort of your own computer.
Everything you Need to Know About Keyword Research
Before you start optimizing, you have to do your keyword homework. Keywords can be tricky; they trend, they change, they grow long-tails...yet keyword metrics are the most valuable data sets you can have before you start optimizing.
SEO experts are well-versed in the data of search metrics, and much of our work involves helping clients narrow in on relevant keywords. But with a keyword research tool like ours, so can anyone else, from content writers to bloggers, or online marketers to webmasters. If you create online content of any kind, you should get comfortable using a keyword tool prior to your content creation.
The best keywords to target are those that your ideal audience is already using to find products or services. It’s important to choose keywords that not only your site stands a good chance for ranking for, but puts your site in front of the audience seeking your product or services. This is where a keyword research tool is necessary.
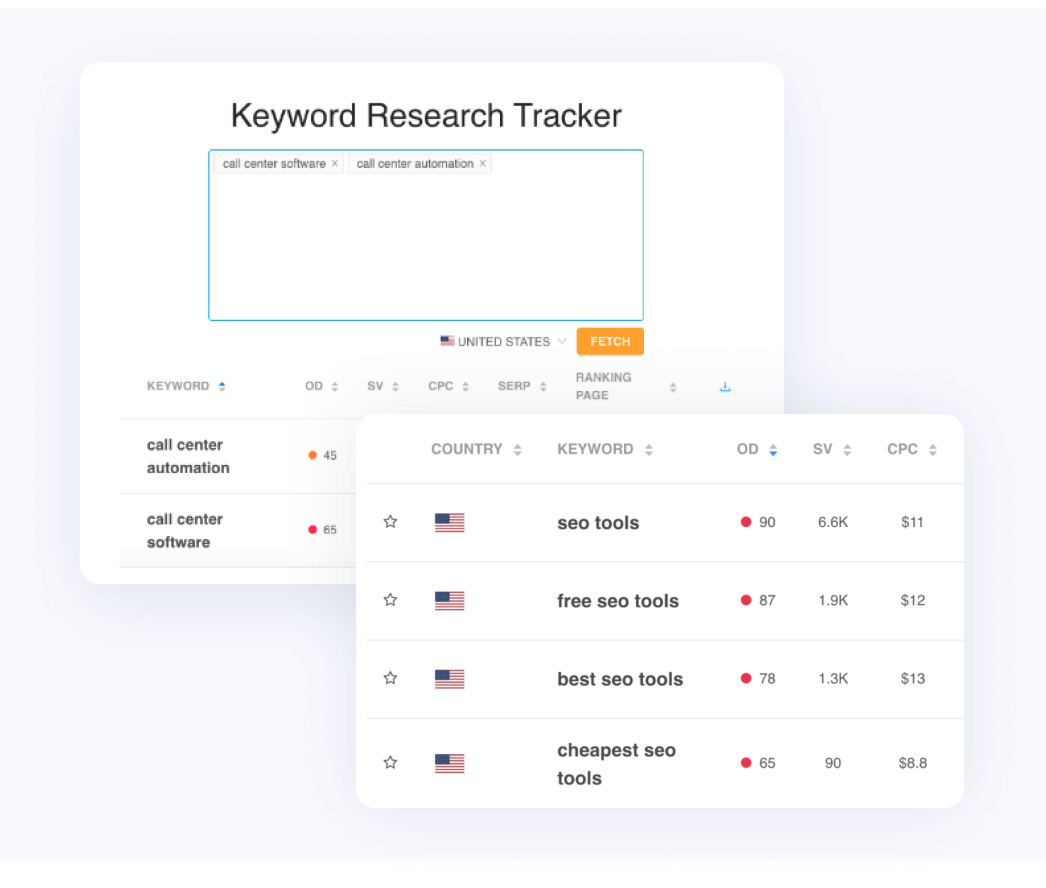
Using a Keyword Research Tool
Keyword research tools are designed to help you make the most strategic decisions about optimization. By understanding key SEO metrics, you will learn which are the most profitable keywords to target to get you in the relevant searches and in front of your ideal audience.
You can utilize our Keyword Research Tracker for free available in your LinkGraph customer dashboard, or you can find another tool that provides the search volume, keyword difficulty, and CPC metrics necessary to make informed decisions about which keywords to target.
In the above images, you will see some keywords alongside their accompanying search metrics. By understanding these terms, you can make some inferences about which keywords provide you the most potential opportunities to rank.
Understanding how all of these terms relate to each other is another important factor in successful optimization. Popular keywords are usually accompanied by higher monthly search volume, but that doesn’t automatically qualify them as the best choice for you. You need to take more than that into consideration when it comes to gaining visibility in the search engine results pages, particularly if you're a webmaster that's just starting out.
How to Evaluate Keywords
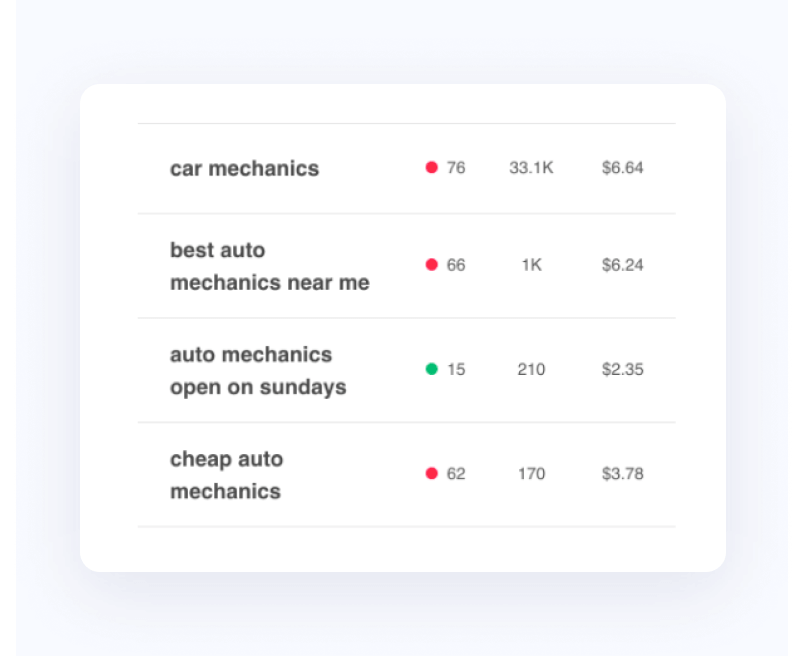
There isn't always a direct correlation between the most popular keywords and the keywords that are the right choices for your website or business goals.
For example, the search phrase, "Discount Shoes," gets 18K searches a month. That's an attractive number of searches, but the competition level for that target keyword is extremely high. Websites like Zappos, DSW, and Famous Footwear have high domain authorities and already occupy the top spots in the SERPs for that given keyword phrase.
When it comes to smart keyword research, the general rule of thumb is this: The best keywords to target are the ones you stand the best chance of ranking for and the best chance of converting from. Every new piece of content you create--whether a new landing page or a blog post--should target a new keyword so you have more opportunities to rank in more SERPs.
The best keywords should meet the following criteria:
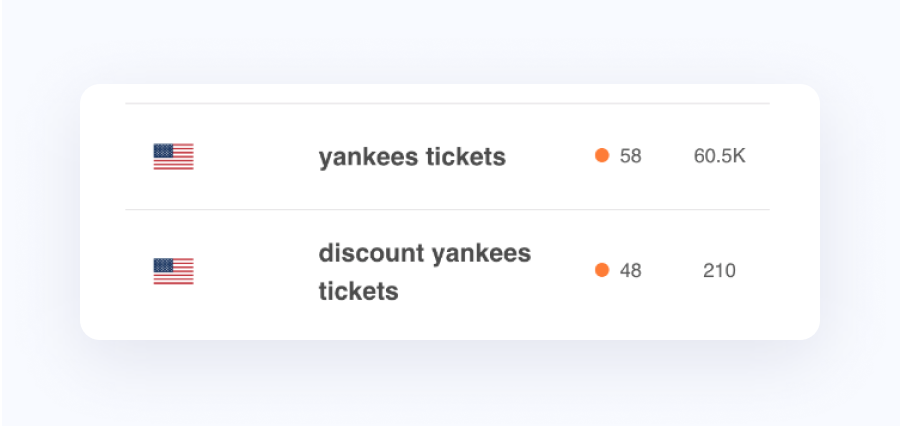
A Little about Long-Tail Keywords
Long-tail keywords can be a great way to make the most out of your optimization efforts. Long-tail keywords are usually search phrases over 4-5 words.
Targeting these long-tail search phrases with blog posts can be very effective because they have a more specific search intent and are far less competitive than other keywords.
Targeting long-tail keywords can also be an effective optimization strategy because it tends to result in higher conversions. Those users who rely on long-tail search queries are usually further down the sales funnel and more ready to make a purchase, fill out a form, or offer an email address.
So I have my Keywords….Now What?
Once you have identified which keywords you want to target, it’s time to transition to doing the work of including those keywords into your content. You need to incorporate your primary keywords in both the primary text of your landing page and the HTML title tags and meta descriptions.
If you use our copy optimizer tool, the process for doing so will not only be easier, it will help you avoid keyword stuffing. Because our tool provides you with the LSI terms that have topical relevance to your webpage content, the distribution of your keywords will appear more naturally and in a way that appeals to search engine crawlers without disrupting the readability or quality of your content.
Optimizing Web Pages for Search
Once you’ve chosen the best keywords, the next step is to start writing and optimizing your landing page copy.
But optimizing content goes far beyond simply hitting a keyword quota. In the early days of SEO strategy, simple keyword stuffing tactics worked, but search engines keep getting smarter and better at understanding the content of a web page.
For this reason, a content optimizer tool like ours can help you include your primary keyword phrases alongside Focus Terms that Google is expecting to see on your landing pages. These Focus Terms are topics, ideas, and phrases that we’ve determined are related and important to the keyword search you’re trying to rank for. Incorporating Focus Terms will help your landing page demonstrate topical depth and expertise.
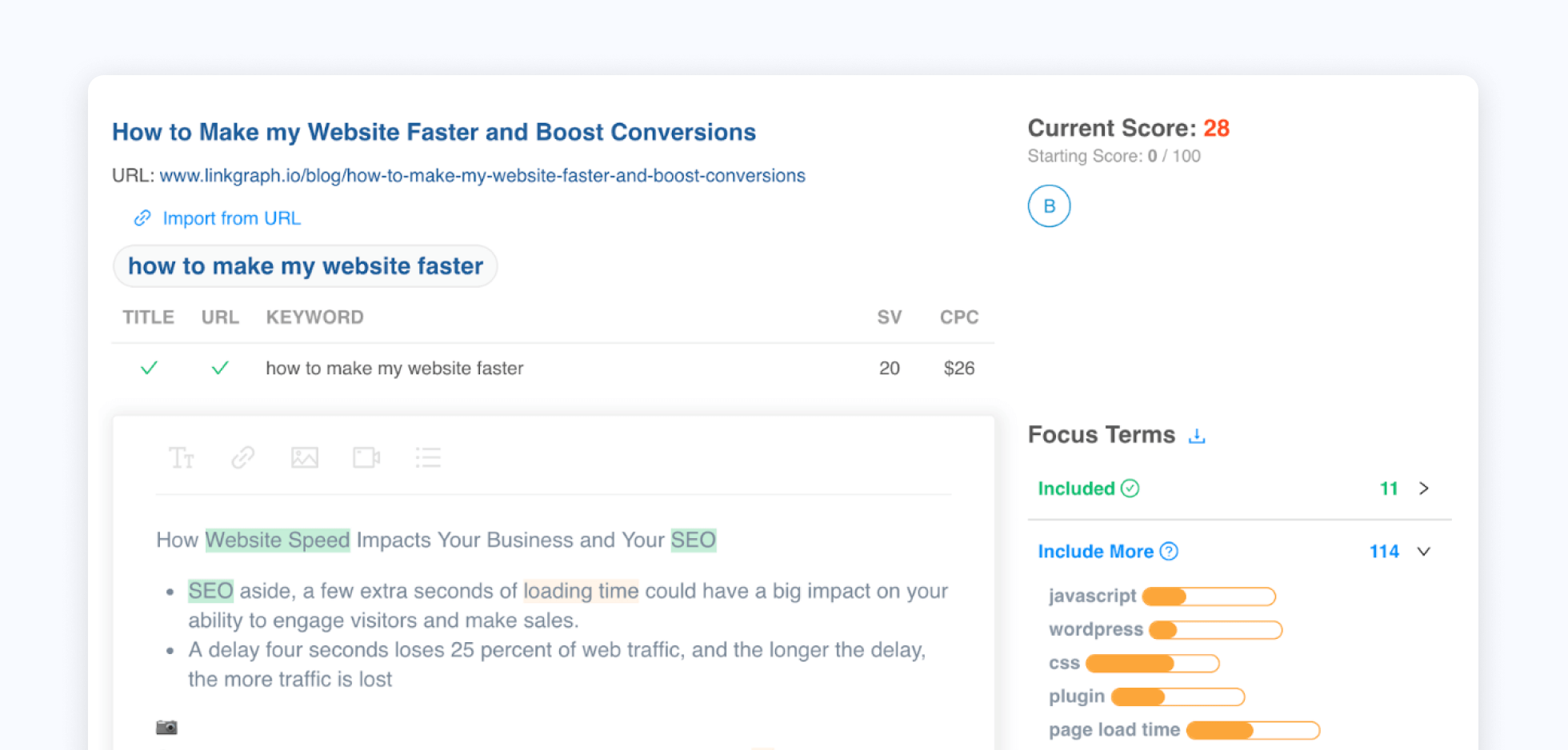
Focus Terms vs. Keywords
Unlike keywords, which are the search phrases you want your own site to rank for, focus terms are semantically related terms that Google bots use to understand the topical depth, relevance, and quality of your web content in relationship to users' search queries. The LinkGraph content optimizer scans the top ranking pages for your target keywords, as well as all of the content on those pages that are appearing in the search rankings, and provides you word suggestions and related topics for the content creation process. Essentially, it helps you create better content in the eyes of Google bots.
High-ranking content often shares certain similarities. Long content, original research and reporting, infographics, and authoritative content all tend to have better content performance in search engine rankings. Google's algorithm rewards quality content, and making your own content more rich and in-depth becomes easier with the help of a SEO content optimizer tool like ours.
Like the Keyword Research Tracker, the copy optimizer tool is available in your LinkGraph customer dashboard. You can also download the LinkGraph Chrome extension to automatically transfer your web page content into our tool with 1 click and start your optimization work right away.
Using the Copy Optimizer Tool
Whether you are creating a brand new piece of content, or revising an existing landing page, our tool makes the process of optimization easy, even for SEO beginners.
As you draft your content, our tool will keep track of the Focus Terms that you have incorporated and will provide you with a content score. Think of it like a content performance score: the higher it is, the more likely your content will get a higher ranking for your desired search term. Even small changes to syntax, vocabulary, complex sentences or phrasing can help you maintain the readability of the content while also optimizing for search.
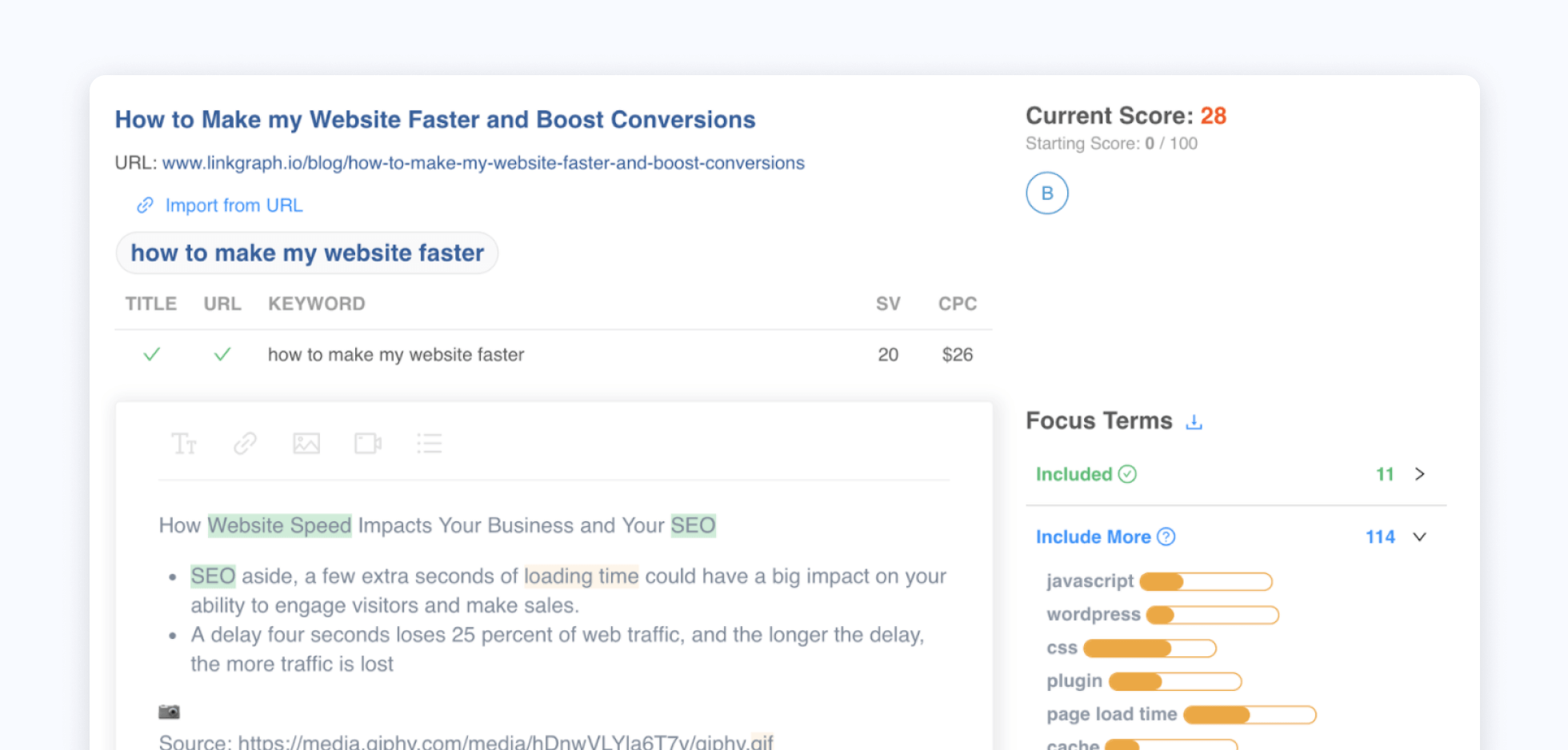
Also, the content optimizer’s color-coded highlighting alerts you to which terms you have sufficiently included, which need to be included more, and which are being overused.

And because the content score takes length into consideration, it encourages you to create more in-depth content that allows the space for the keywords to naturally appear. Longer content tends to do much better in search, so our copy optimizer uses 2500 words as an ideal benchmark. The tool will also provide you with an overall Content Score. A score over 80 is considered very good.
Whether you want to update a page of content that is already on your site or use our Focus terms as a starting point for new ideas, our tool is the easiest way to see SEO success in not much time. In the below video, you will find a tutorial on how to use the copy optimizer tool to create the best content on your landing pages.
If you are optimizing an existing piece of content like your site’s homepage or current landing pages, adding our copy optimizer chrome extension to your toolbar will allow you to automatically transfer the content of any existing landing page into our tool and start your optimization work from there.
Additional Considerations when Optimizing Content
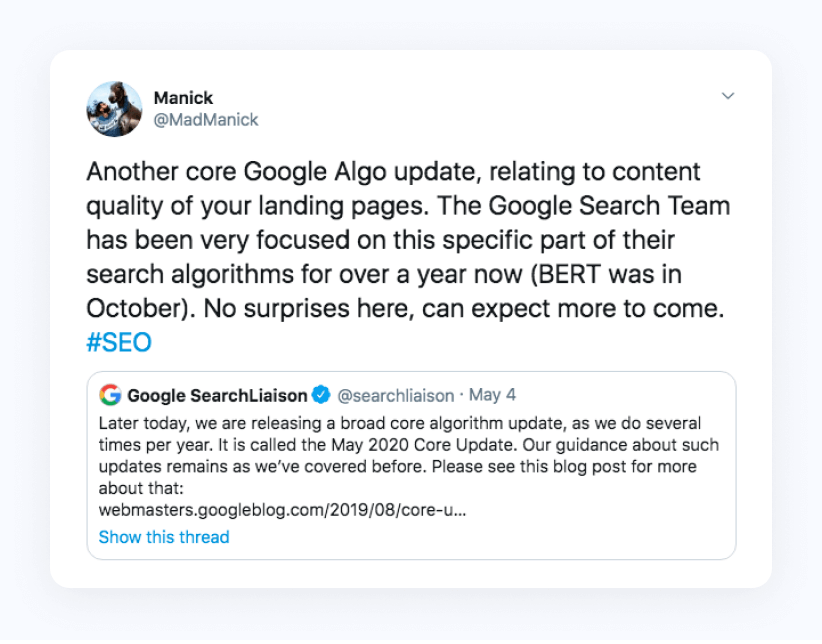
Starting in 2017, Google’s search quality teams have been specifically focusing their engineering efforts towards content-quality signals and have pushed core algorithm updates every quarter. Their BERT update in October 2019 was one of the most meaningful content related updates they have rolled out in years.
Bert has helped Google crawlers understand language and keyword usage the way that human's use it. Google will continue to do a better job of identifying quality content among its index as algorithms and content-quality signals become even more refined. For this reason, the sole focus of your copywriters and content team should be to simply create great content, because creating high-quality content is essential to the success of your optimization efforts in the long run.
Although quality may feel subjective, Google's webmaster guidelines are clear about what quality looks like in the eyes of Google bots. Search engines want to rank good content, and they look for hints about the quality of every web page they index, from headlines and subheads to keyword density and url structure. Each element of website optimization communicates to Google whether your content will keep readers' attention and whether they will find your content valuable and useful.
Factors like content uniqueness, content length, external and internal links, anchor text, headings, grammar, syntax, and readability all influence whether or not your content ranks. On their blog, Google advises webmasters to consider multiple questions about the pieces of content they create.
- Does the content provide original information, reporting, research or analysis?
- Does the content provide a substantial, complete or comprehensive description of the topic?
- Does the content provide insightful analysis or interesting information that is beyond obvious?
- If the content draws on other sources, does it avoid simply copying or rewriting those sources and instead provide substantial additional value and originality?
- Does the headline and/or page title provide a descriptive, helpful summary of the content?
The Importance of Internal Linking
Internal linking is when you include a link that directs to another page on your site. It not only directs your users to contextually relevant content, it helps communicate to search engines your website architecture. It also spreads around your link juice--or the search equity passed from one page of your site to another.
Google uses a metric called PageRank to understand which pages are most important. Pages that are closer to the homepage of your site, like those linked to in your navigation menu and footer, as well as pages that you internally link to frequently have more PageRank. Google uses the amount of PageRank on your pages compared to the amount of PageRank on your competitors pages as a component of its ranking algorithm.
There are ways to use internal links to direct landing pages with higher PageRank to the most important pages on your site. For SEO purposes, you can evaluate content performance primarily through keyword rankings, or determine highest-performing pages through conversion rates. Then, direct PageRank toward those important pages to get them ranking more often. This is an advanced strategy and should only be implemented by SEO pros for the best results.
The anchor text of your internal links, as well as the semantic context surrounding them, are important indicators to Google about what type of information your pages contain and help them understand what type of searches they could be relevant for. These internal links also allow you to demonstrate topical depth and authority for your target keywords.
Outside of your navigation bar, blog posts are good opportunities to internally link to related high-value landing pages on your site. Do you have another post that explains a certain concept with more detail? Or do you provide a tool or service that can help meet a user’s needs? The more content that you create, the more important internal linking becomes, as it serves as a kind of directory for your users and shows search engines that your site has topical depth in your niche or vertical.
Optimizing HTML Tags and Technicals
When it comes to optimizing HTML tags and technicals, non SEO experts may feel intimidated to start making changes or adjustments to source code. But if you have a CMS like WordPress, making adjustments to your tags is very simple.
Remember that when search engines crawl your site, they look to the source code for key information about your website’s content and relevance to specific search queries. Taking the time to ensure your target keywords are included in your primary HTML tags is an essential step in seeing tangible results in increased organic traffic.
Content Management System and Hosting
The majority of webmasters use a content management system (CMS) like Wordpress to manage their website. Depending on your CMS, you should be able to specify your title tags, meta description, and HTML tags fairly easily.
When it comes to optimizing the onsite technicals of your website for search, having some familiarity with your CMS will be necessary. We use a modified version of Wordpress for most of our clients given it’s flexibility, ease of use, and performance. We’ve done optimization work inside other website builders like Wix, Squarespace, Weebly, and Shopify, and have generally found that the lack of direct control over the hosting environment and server limit the SEO capabilities of these platforms, and we would not suggest them for enterprise-grade organizations.
- Yoast SEO or All In One SEO: Allow you to set up your SEO meta tags across your landing pages, as well as a sitemap, robots.txt, and structured data.
- Redirection: Great for managing redirects and will automatically create redirects for you when you update permalinks on your pages and posts.
- WP Rocket: This plugin gives you a lot of performance optimization features for free.
- SeeRobots: Easy way to see the robots policy of the page you’re viewing without having to inspect the HTML content.
- LinkGraph Chrome Extension: Our free SEO chrome extension that lets you view keyword search volume and CPC data directly inside search results, and also allows 1-click importing of landing page content into the content optimizer for analysis.
- BuiltWith: Shows you what technologies the webpage you’re viewing was built with.
- Lighthouse: The PageSpeed Insights scores for your website on mobile and desktop are important performance benchmarks.
It’s also important the hosting environment you’re running your website on is performant and follows certain best practices. Here’s a checklist of key functionality you need to have:
Optimizing Title Tags
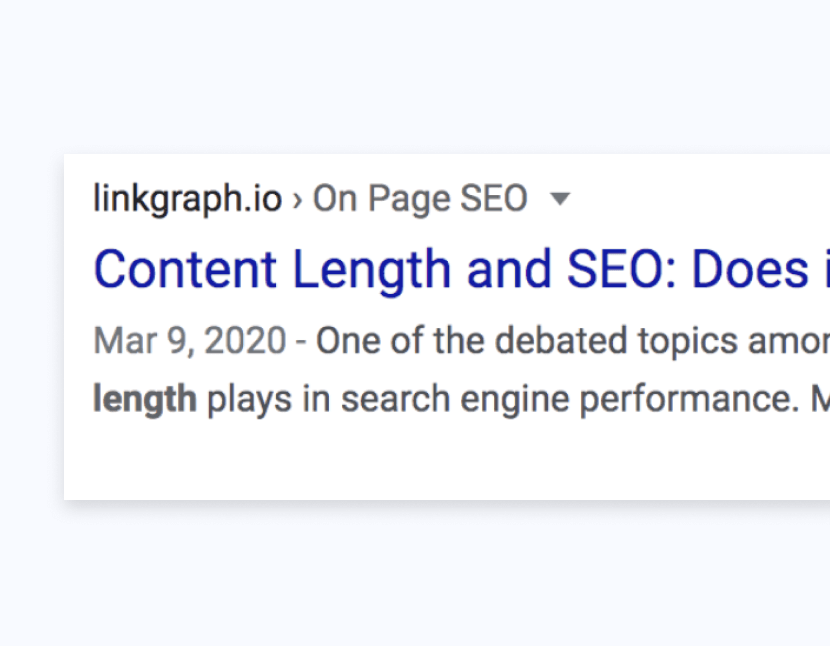
The title tag is the HTML code that determines the title of a web page. Here is an example of what a title tag looks like in source code.
<title>
Content Length and Seo: Does it Really Matter?
</title>
And here is an example of how a title tag looks when your users see it in search results.
The primary reason title tags are so important is because they influence whether or not users click on your web page in the SERPs. This is known as click-through-rate (CTR), or the ratio of those users who see your web page in search results and the number of those who click on it.
A strong click-through-rate means your search is meeting the needs and desires of those utilizing the search phrases you rank for. You can find your CTR data in Google Analytics. If your CTR is low on certain webpages, it is your hint that you may want to consider changing your title tag or meta description to be more appealing to users.
In order to optimize your title tag, you need to include the target keywords you are trying to rank for. If you have a WordPress site, your title tag will be automatically generated from the title you give your HTML document in the designated text box. To optimize effectively, you need to determine a title that both includes the primary keywords and compels your users to click.
Google will display approximately 60 characters of your title tag. According to research, about 90% of title tags display properly. You want your title tag to appeal to users and search engines, so here are a few areas to focus when writing them.
- Length: Google will cut off title tags that are too lengthy, so keep it short and sweet
- Keywords: Put the most important keywords first, but avoid keyword stuffing. Use synonyms when necessary, and avoid bold fonts or capitalizations
- Uniqueness: An original, relevant title tag will appeal to users and entice them to click
Optimizing Meta Descriptions
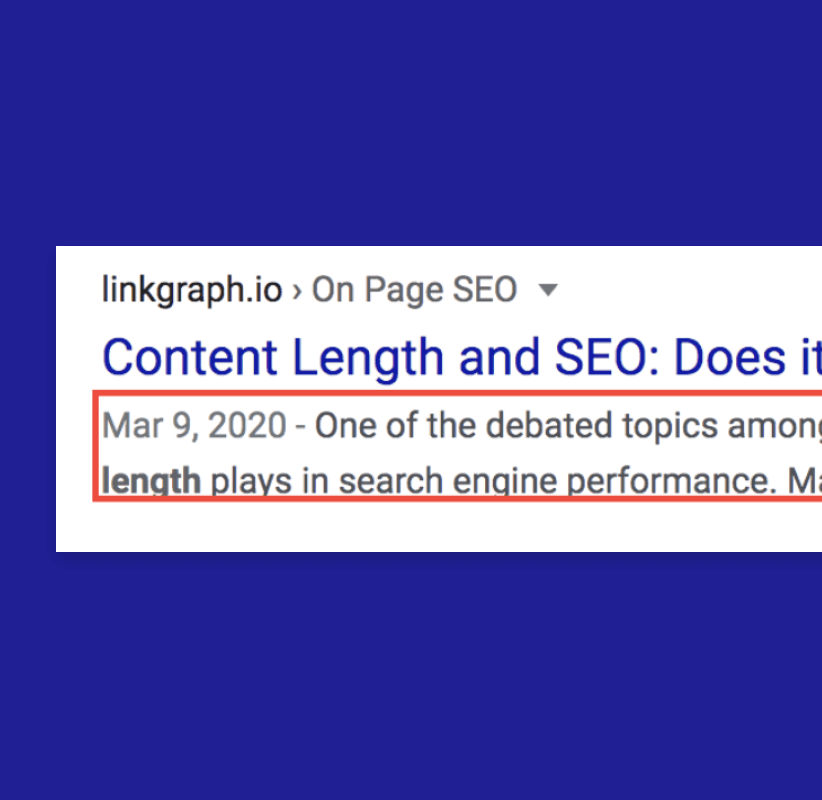
The meta description is the 160-character snippet that appears below your title tag in search results. In the below image, you will see the meta description from our previous example highlighted in red.
When it comes to optimizing this description, you should consider both your readers and search engines. This meta description should give users a brief summary of the content of your web page and entice them to click. If you are using a Wordpress site, you will find a clearly designated textbox in which to enter your meta description. The CMS will take this content and embed it into the HTML source code as a meta tag.
Although Google no longer considers meta descriptions as a direct ranking factor, they do influence your CTR and so have an indirect impact on your rankings. Google also generates rich snippets from meta descriptions. Those websites with Structured Data Markup can help communicate to Google the most important parts of their meta descriptions to highlight.
You will see that in our search result in the above example, Google rich snippets emphasized the words “content length,” and “SEO,” in bold font. Seeing those are the keywords we were hoping to rank for with this particular blog post, we can see the tangible results here of our optimization efforts.
Heading Tags
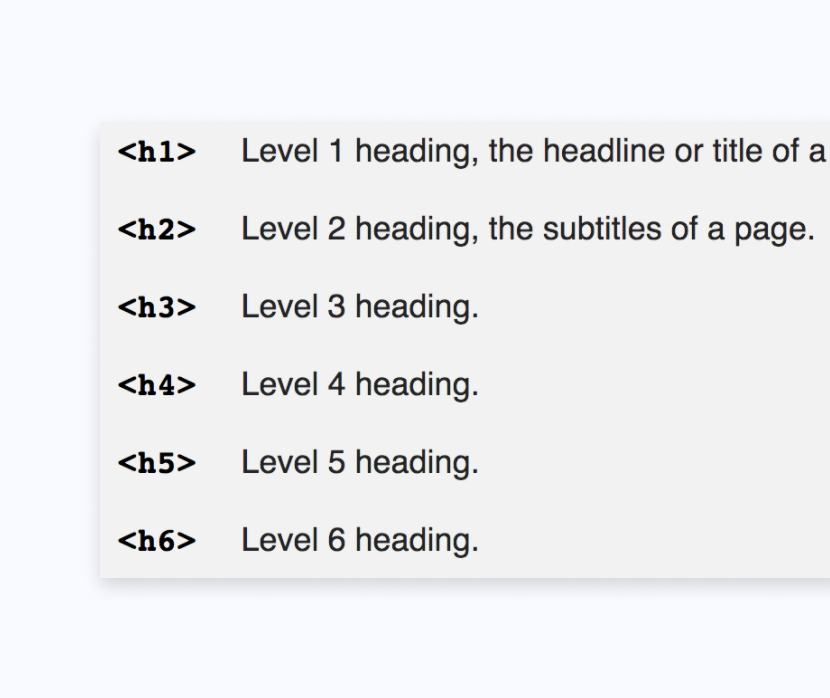
Heading tags structure your web page content for the benefit of both readers and search engines. Although your heading tags are not visible to users in search results, Google bots do crawl them and use them to determine the content and quality of your website. Here is what heading tags look like in source code. In a content management system, you will be able to easily designate your h1 tag - h6 tags. However, including your one or two primary keywords over and over again in these headings will look like obvious keyword stuffing, which is a major no-no for Google.
This is where our Content Optimizer’s Focus Terms terms come in handy. Using Focus Terms in your headings will help emphasize to Google the topical relevance of your content to the primary keyword you want to rank for without having to over-rely on that keyword. Google is getting smarter every year and can now understand contextual relevance and synonyms with far more nuance, which is great, because it means you don’t have to exchange bad writing for ranking.
In our copy optimizer tool, there will be a list of suggested Focus Terms provided to you based on your target keywords. If you use the tool to draft your web page content, it’s very easy to include those terms into your heading tags.
Schema.org Markup and Rich Snippets
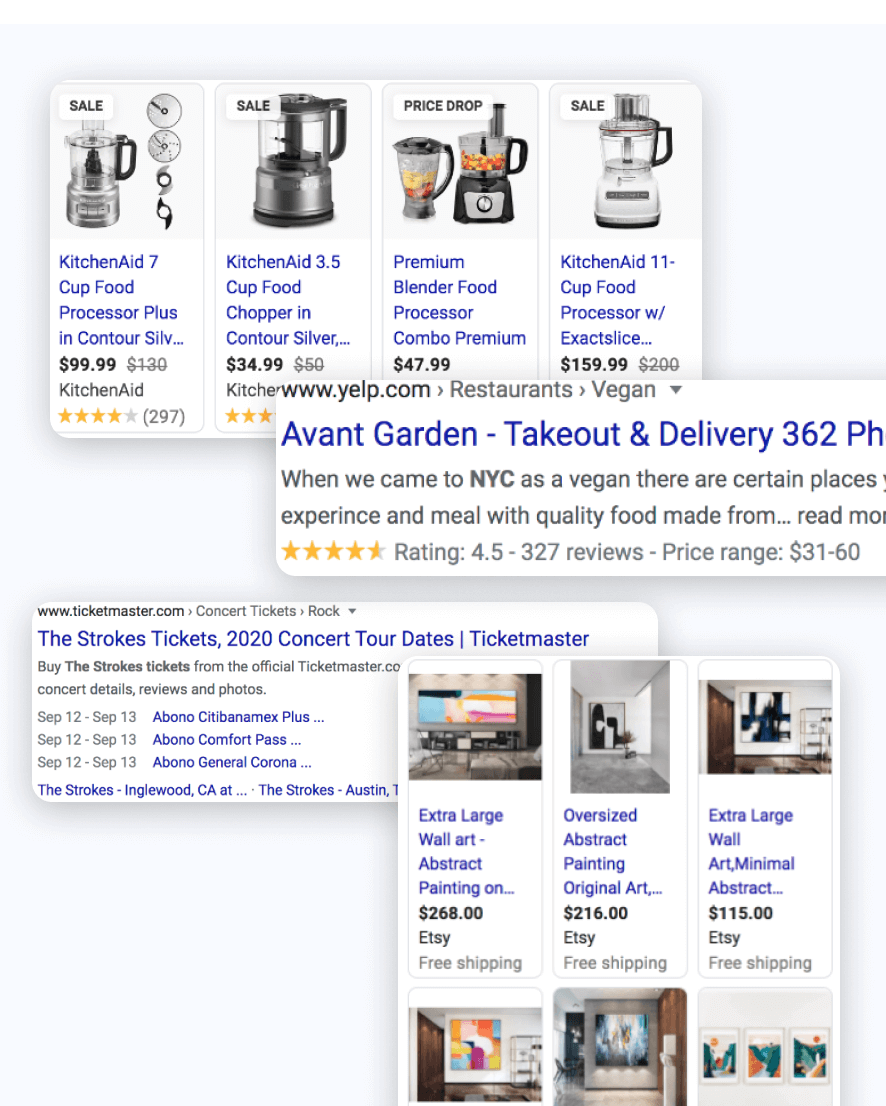
In order to make content on the internet more structured and search engine crawler friendly, search engines adopted the Schema.org standard to create a universal HTML microdata format for webmasters to utilize to communicate specifically with crawlers.
Rich snippets in search results, such as reviews, ratings stars, event sitelinks, product information, FAQs, social media profiles, company business details, and even a site-search box are some examples of commonly utilized schema markup by Google. Not every site will be able to utilize all of these, but utilizing the ones that apply to your website can be a powerful way to improve your CTR, traffic, and rankings. Here are some examples of rich snippets in Google search results.
You can utilize our Rich Snippets Validator tool to get a sense of how structured data markup could benefit your site with better rich snippets in search results.
Using Google Analytics to Monitor Your Optimization Efforts
You will never know whether your optimization efforts are worth it unless you have the proper platforms to measure your results. Google Analytics and Google Search Console are free services that will provide you valuable data about your target audience and your organic search traffic.
We could write a whole EBook about how to get the most of these powerful platforms, but we’ll just mention them in passing here to make sure you have them setup and configured properly for your website.
Getting comfortable using and understanding the features of these essential tools will allow you to know whether your optimization efforts have been successful. Measuring the results of your optimization efforts will help you continually refine your strategy so you continue to experience growth for the long-haul.
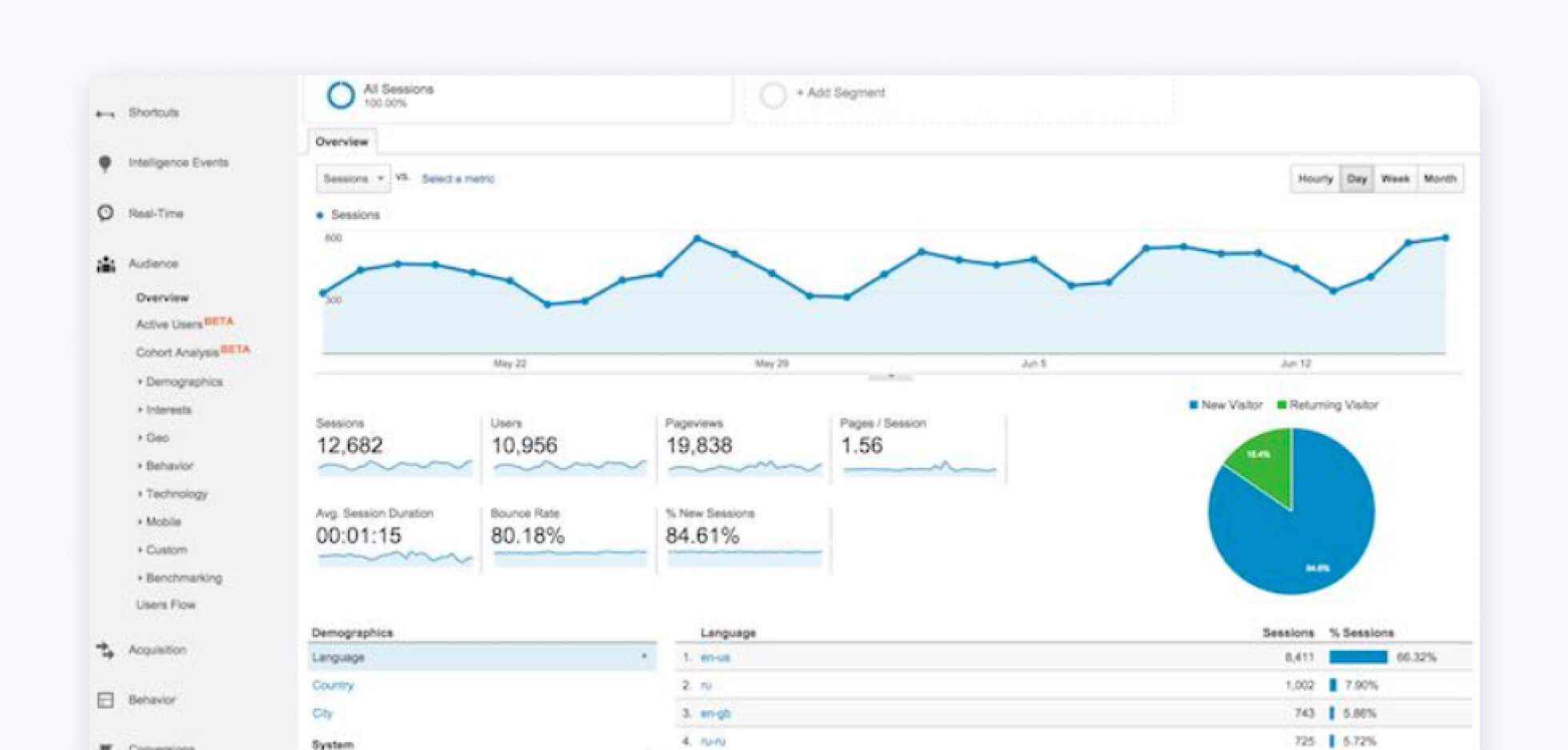
Google Analytics
Google Analytics will provide you essential information about organic traffic, your users, and how they are interacting with your content. Metrics like CTR, page views, sessions, pages per session, bounce rate, and others can help you understand the impact of your optimization efforts and where you can improve.
If you want to understand your site visitors’ browsing experience, like what behaviors they take on your pages, how long they spend on specific pages, and at what moment they leave your site, Google Analytics is the first place you should go to access this valuable data. From an SEO perspective, there are no better insights available about your web traffic then this free tool.
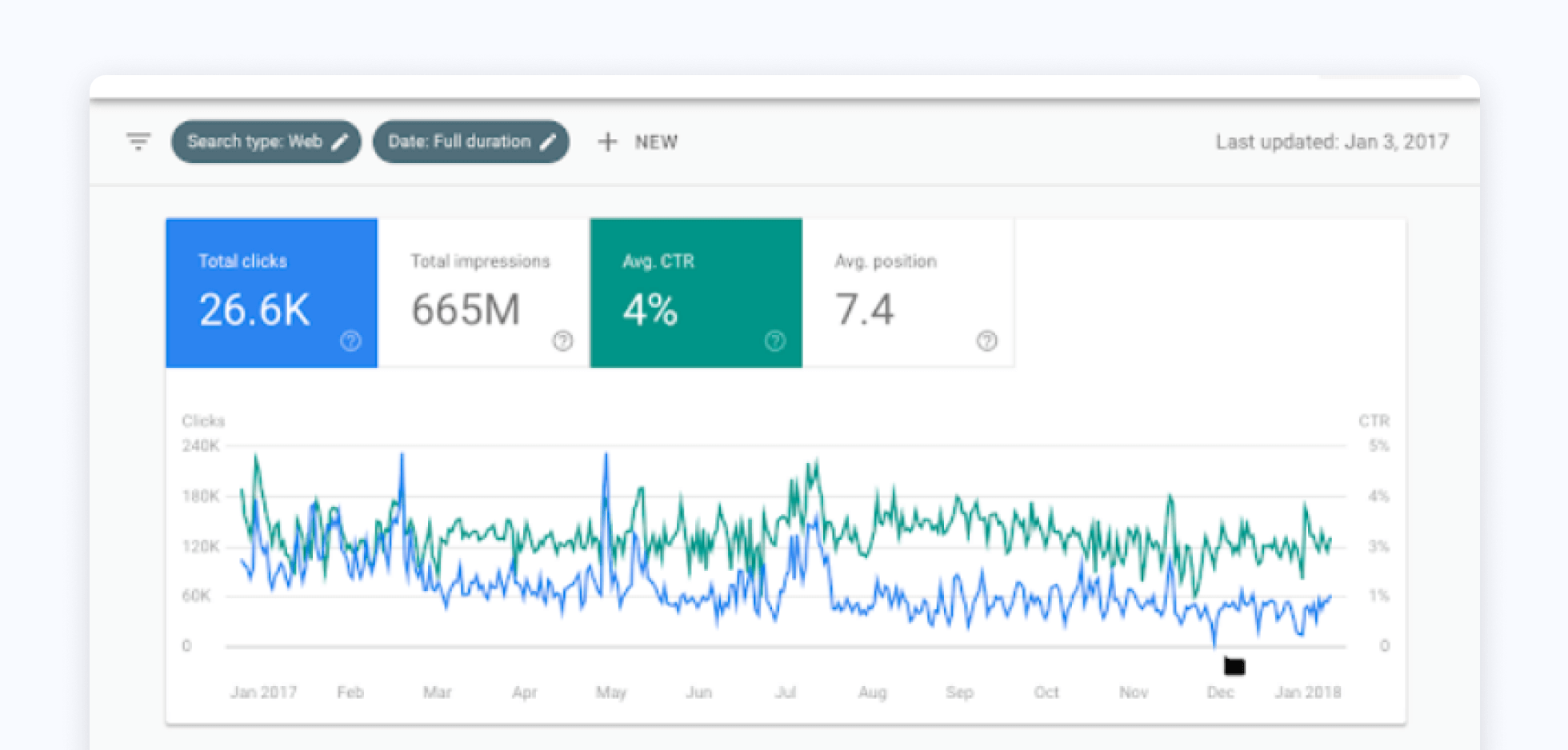
Google Search Console
GSC is a platform designed to help you improve your website’s performance in search engine results. With GSC, you can submit sitemaps, access crawling and indexing data, and improve your mobile usability. GSC provides rich insights into how to improve your rankings, alerts you to problems or issues, and helps you better understand how Google understands your website content overall.
Google Search Console is the only source of truth for your keyword rankings on the internet. If you want to know what the Google rankings are for your website up-to-the-day, this is the platform that will help you make granular changes and do the performance benchmarking and A/B testing necessary to maximize your on-page optimizations to produce maximum results.
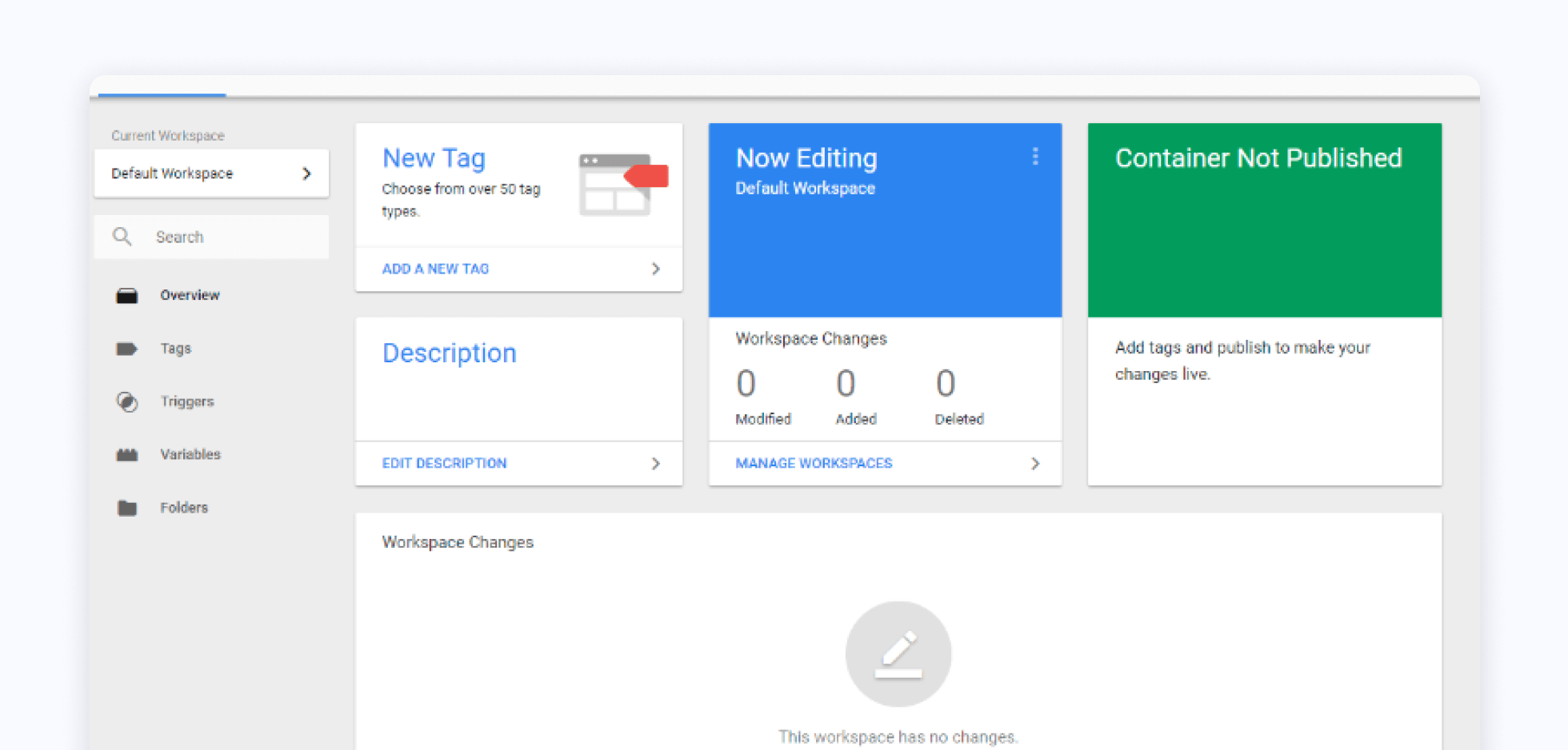
Google Tag Manager
Google Tag Manager is a management system that allows you to manage the tags -- or fragments of code -- on your website or mobile app. The platform is a great beginner's guide to using tags on your website.
All of your marketing pixels and Javascript code should be hosted inside a Google Tag Manager Container. If you’re still asking your development team to add new vendor libraries for analytics or measurement, it’s time to migrate to GTM. GTM is the gold standard for high performance marketing teams who iterate quickly. Since GTM is free, there’s really no reason not to be using it.