Content Pruning Guide for Content Managers and SEOs
If you’re looking for ways to improve the SEO of your website, content pruning is an effective method to consider. Content pruning is all about removing any […]
If you’re looking for ways to improve the SEO of your website, content pruning is an effective method to consider.
Content pruning is all about removing any unnecessary content from your website, which can help your website rank higher in search engine results and can also improve user experience.
In this article, you will learn how to do content pruning for SEO, from identifying what needs to be pruned to taking steps to ensure that it’s done correctly. Keep reading to find out more.
What is Content Pruning?
Content pruning involves a thorough review of all content on a website to identify any content that could be seen as irrelevant or low quality from the perspective of search engine algorithms. Once identified, content pruning involves removing those low-quality pages from the website or replacing them with better content.
A part of regular website maintenance is making sure that all of the content on the website is up-to-date and relevant to the website’s goals. This can help ensure that a website has content that is useful to its visitors and provides value to users who arrive from search engines.
By removing low-quality or outdated content, websites can see improved search visibility for their highest-value, highest-converting web pages.
Why Remove Content From My Website?
Content production takes time and resources. So you may be wondering: Why remove content from my website after all the work it took to create it?
Although it may feel counterintuitive to your content strategy, content pruning can actually have major benefits to your search engine performance. This is even more true for websites that have a robust SEO content strategy and are publishing new web pages on a regular basis.
Some of those benefits include the following:
- Improve a website’s visibility by allowing search engines to index your best and highest-converting web pages
- Ensure visitors are presented with the most up-to-date information
- Provide higher-quality content and a better user experience
- Prevent visitors from seeing any low-quality pages
- Ensure your crawl budget is spent on rank-worthy content
Any content that sits on your websites that doesn’t pull its weight in either traffic or conversions isn’t actually bringing value to your business.
By taking the time to regularly prune their content, content managers can ensure that their website is performing at its best. That’s why sometimes content pruning is the right choice for your content strategy.
What Makes a Web Page Prunable?
Here are some of the qualities to look for when searching for content on your website that may need to be pruned.
Low-Quality
Bad content can have a negative impact on a website’s rankings. Low-quality content can include pages with duplicate content, thin content, or other qualities. It can also include pages that are not user-friendly or are low on useful information. Content pruning can help to identify and remove such pages, allowing search engines to easily index the more relevant, more quality content on the website.
Duplicate Content
Duplicate content is web pages with the same content or similar content that search engine crawlers do not identify as distinct. Google does not want to see duplicate content on a website unless it has been clearly identified as such via a canonical tag.
Thin Content
Thin content is often short-form content that doesn’t provide any real value to the user. Although there is no exact content length that Google privileges in search engine results, experiments have shown that longer, in-depth content tends to rank higher.
Most often, thin content can be combined with other pages on your website to provide a more comprehensive, in-depth answer to a topic, question, or keyword query. Combining content, or redirecting thin pages to more in-depth ones, are also a part of the content pruning process.
Outdated Content
The reality is, the content on our website will become outdated over time. This is why creating evergreen content is important, however, it’s unlikely that your long-form content will last forever without the need for updating. Trends, technologies, and knowledge will change, and web pages should include the most up-to-date, useful information for search engines.
Also, outdated information can be confusing for visitors and lead to a poor user experience. Removing outdated content can ensure that visitors are presented with the most relevant and useful information.
Under-performing Content
If you have a web page on your website that does not get traffic or conversions, what value is it bringing your business? If the web page does not rank in search results, convert users, or is not a vital part of the buyer journey, it doesn’t really have a place on your website unless you take the time to improve its content.
How to Find Pages for Content Pruning
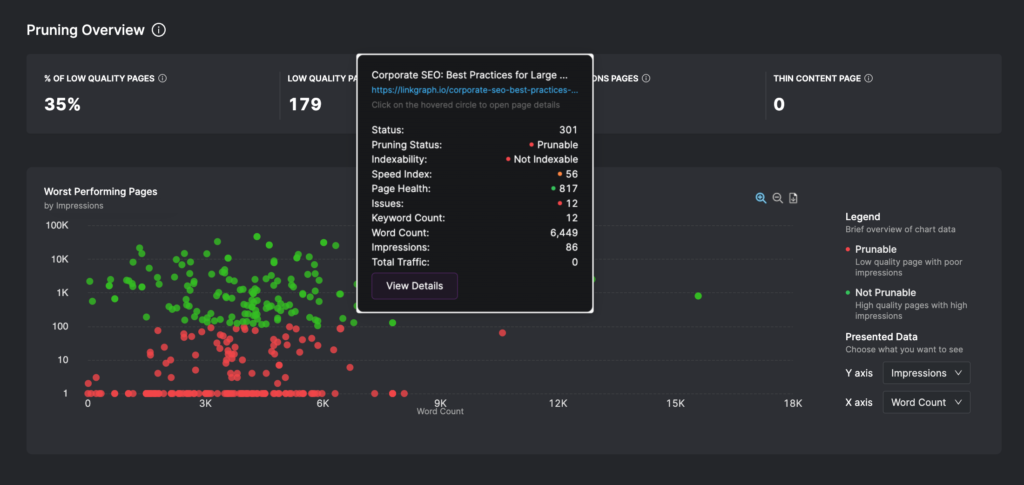
You can use the Page Pruning tool in the Search Atlas dashboard to discover pages that may be eligible for content pruning.
To find the tool, navigate to Site Auditor > Page Pruning.
This tool will show you any pages that are eligible for pruning due to a variety of reasons:
- Low organic impressions
- Low clicks
- Indexability
- Total ranking keywords
- Average position
- Content quality/scores
Remember, just because a page appears on this list doesn’t mean that it has to be pruned/deleted, but that it may be eligible based on its performance metrics.
Next Steps for Page Pruning
Once you have reviewed the software’s suggestions and confirmed that the pages are eligible for pruning, here are the next options for you to take.
1. Improve the Content on the Page
The underperformance of the page may rest in the fact that the content is thin or is not providing a comprehensive answer to the user’s questions.
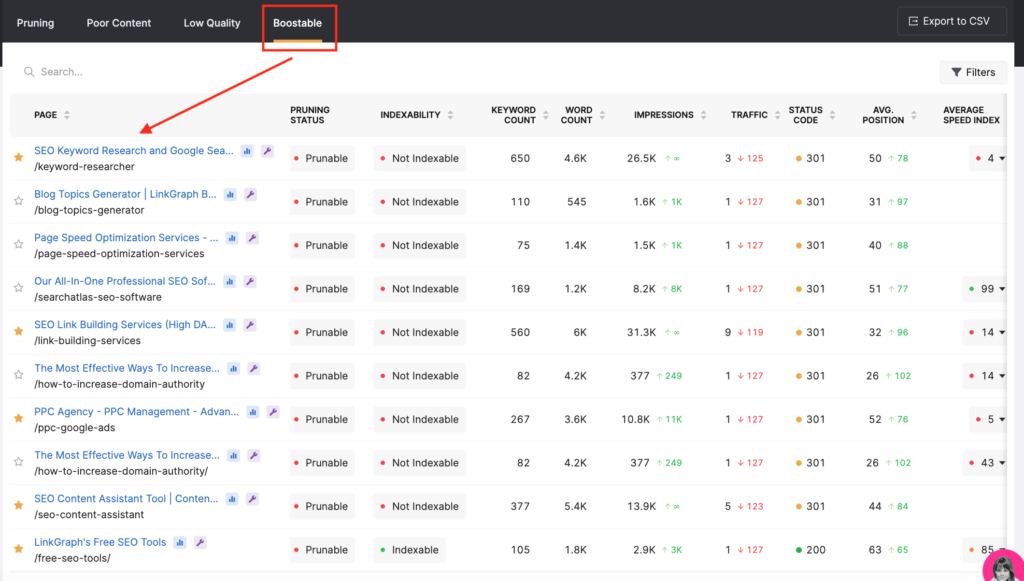
You can look to the “Boostable,” tab in the Page Pruning tool to identify those pages that just might need a slight content score boost.
The URLs that are listed here are already earning organic impressions but are not seeing as much success in organic traffic. Most likely, Google sees those pages as relevant but is not ranking them on the first page as a result of the content.
You can use the SEO Content Assistant in your Search Atlas dashboard to discover ways to strengthen and improve your content. Or, use the on-page audit tool to see what on-page elements may be impacting your performance.
Follow the guided suggestions for focus terms, headings, questions, and internal links. Include them on the page to make the content more rank worthy.
2. Update the Content to be More Evergreen
If your content covers trends or keywords that have seasonal search volume, that may impact their underperformance.
Consider updating the content with more evergreen information so the content has a longer shelf life in the SERPs.
Also, make sure that the information on the page is up-to-date with accurate, relevant information. Over time, links may break or content may become outdated. Updating your blogs and articles every 1-2 years should be a part of your regular website maintenance.
3. Build Backlinks to the Page
If both the SEO Content Assistant and on-page content school confirm that your content has high scores and is rank-worthy, you may just need a bit more of a link boost.
Backlinks are Google’s number one ranking factor. If you don’t have very many backlinks pointing to your web page, that may be a reason why it is not ranking on the first page.
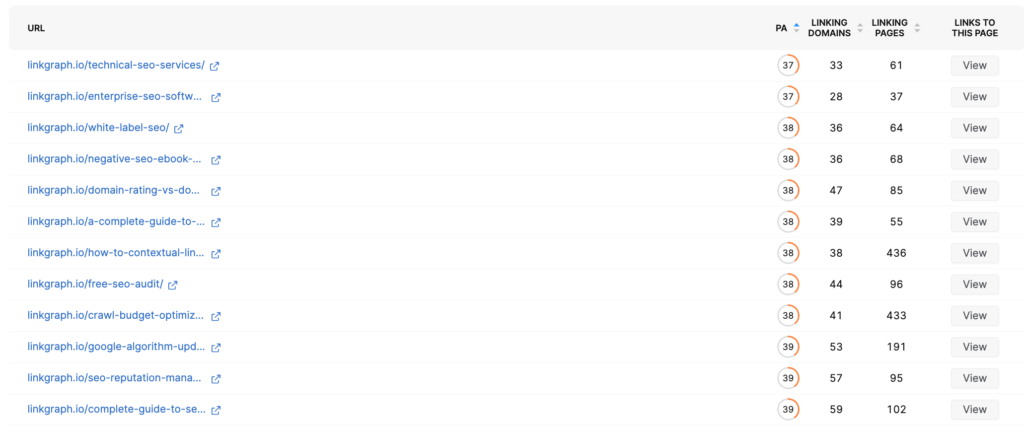
You can use the backlink research tool in your dashboard to see which of your web pages have the least amount of link equity.
Consider investing in a link-building campaign in order to improve the off-site signals of the content. Doing so is likely to improve the overall keyword rankings, impressions, and organic clicks.
4. Reoptimize the Page for a Different Keyword
Another possible explanation for your content’s poor performance may be keyword related.
Some keywords are more competitive than others. If you optimized the page for a keyword that is out of reach, reoptimization may be your next step.
When choosing keywords for SEO, you want to make sure your website has a realistic chance of ranking for the target keyword. Websites with higher Domain Authority will stand a better chance of ranking for competitive keywords.
At LinkGraph, we suggest keywords that are less than or equal to your website’s Domain Authority.
So once you find a more realistic goal, optimize for that keyword instead. This will likely involve changing metadata, website copy, and headings on the page. But it can make a huge difference in improving organic performance.
5. Redirect the Page to a More High-Quality One
A page may be flagged for pruning because Google is ranking a more helpful piece of content on your website.
This is known as keyword cannibalization. It happens when two pieces of content are very similar and Google doesn’t know which to promote. If there is a page that is ranking less often but is similar in relevance, you can do your “content pruning,” by adding a 301 redirect from the less comprehensive page to the better performing.
6. Combine Thin Content into a More Comprehensive Resource
If you have a series of pages that are thin on content but relate to a similar cluster of keywords, consider combining those pages into a more useful, long-form resource.
Why? Because Google likes to promote content that satisfies users’ search intent. That means not only answering their initial questions but all of the additional questions that might follow regarding that primary topic.
So before giving up on that set of keywords entirely, combine those various pages into one page. Then, see if the overall keyword rankings improve.
7. Consider Removing the Page Entirely
This is the last step you want to consider after you have concluded that none of the above steps help to elevate content performance.
The reality is, if a piece of content is not driving website traffic, converting users, or an essential part of the buying journey, it doesn’t really deserve space on your website.
Take the ultimate step and trim that content branch off your tree.
Conclusion
Making content pruning a regular part of your website maintenance is a good habit to get into. This is especially true for websites that publish a lot of content and have a robust SEO strategy.
You can also use the same Search Atlas tools to scale up your content marketing and blog strategy. Connect with one of our product managers to learn more about our enterprise SEO software platform.