GPT-3: The 5 Things SEOs & Digital Marketers Need to Know
Learn about the world’s largest natural language processing (NLP) model — GPT-3 — and how it’s impacting the SEO and digital marketing industries.
The artificial intelligence research laboratory, OpenAI, released their GPT-3 model as a commercial product in 2021. So far in 2022, the wide availability of GPT-3 is already transforming the SEO and digital marketing industries.
Many software engineers have already customized GPT-3 to fit their applications. Tools like Search Atlas, Copysmith, Jasper and others are using GPT-3 for their AI-generated content generators, empowering content marketing teams to create content at scale.
Digital marketers and SEOs should familiarize themselves with the GPT-3 model and anticipate its many applications to our industry. Here are 5 things SEOs and digital marketers need to know about GPT-3.
What is GPT-3?
At its most basic level, GPT-3 is a text generator. Give GPT-3 an example of what you would like it to write — whether a business report, a Dr. Suess poem, or any other type of content — and it will identify the language patterns and return a text completion.
Why Does GPT-3 Matter for SEO?
Content creation is a fundamental pillar of SEO strategy. Because GPT-3 produces content based off just a few inputs, the use cases in SEO are significant. Blogs, meta descriptions, landing page copy, and more can all be generated by this AI technology.
For those SEOs who want to scale up their content production to better compete in search, GPT-3 powered content generators are the way to do it.
But before content marketing teams start replacing their writers with robots, here are 5 important things to know about GPT-3 and SEO.
#1: GPT-3 is the Biggest Language Model Ever
GPT-3 is the largest NLP model ever created. It’s over 100 times larger than its previous version, GPT-2, and 10 times larger than its closest competitor, Microsoft’s Turing NLG. With 175 billion parameters, GPT-3 has ingested nearly everything published on the internet. It also cost around $12-million dollars to train.
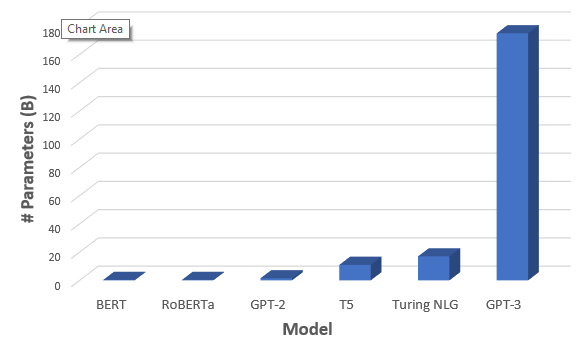
To put the potential impact of that size into context, think back to Google’s BERT. Although BERT shares a similar architecture to GPT-3, BERT is significantly smaller. In 2019, the BERT update impacted 10% of all search queries, helping to provide even more relevant results to users because of its more nuanced understanding of complex syntax and prepositions.
GPT-3’s sheer size is the primary reason why it is a better performing NLP model than others we’ve seen. It is essentially the most literary, well-read robot ever.
If BERT could have such a significant impact on the quality of the search experience, imagine how a model as large as GPT-3 is elevating the performance of those applications that rely on AI text prediction — like call centers and chat bots. The GPT-3 commercial product has providing developers across industries with a newer, far more efficient product.
#2: GPT-3 Is Really Good, But It Still Needs A Human Touch
GPT-3 has been trained by both the highest-quality content on the internet — think reputable online newspapers — and also the lowest quality content (Forums, blogspots, etc.) Although GPT-3 is really amazing at generating text, it does have some kinks and lacks the reasoning to avoid glaring, simple mistakes.
Unlike a human, GPT-3 cannot evaluate whether the text it generates is offensive, discriminatory, fake, or even just flat-out illogical.

OpenAI has certainly created a model that sounds more human-like, but actual human oversight and curation is still necessary for the product to function correctly and “for the good.” At times, GPT-3 can produce low-quality, unreadable content, which is the opposite of what Google looks for when ranking pages.
For that reason, it’s best that content marketers use GPT-3 generated content as a starting point. Topic generation, first paragraph, first drafts, or meta tag generation can all be significantly sped up with the help of a AI-powered content generator tool.
But make sure there are still some humans left around on your team to edit, enrich, and revise any AI generated content.
#3: The Use Cases For GPT-3 in SEO Are Significant
The amount of tasks that GPT-3 can accomplish are truly impressive. For example, GPT-3 can function as a search engine.
It can generate code.
It can do UI/UX design.
Other use cases for GPT-3 in digital marketing include:
- Content Optimization
- Technical SEO
- Content Strategy
- Keyword Research and Clustering
- Ad Copy & A/B testing
- Social Media copy generation
- Web Development
- And others!
Those SEO agencies and digital marketers who incorporate GPT-3 powered tools into their workflows are likely to see faster and increased content production. For those teams without the resource in-house, these tools can be huge to scaling growth and competing in search.
#4: Yes, GPT-3 Could Reduce Content Marketing Jobs
The reality is, anyone who relies on content writing from freelancers or low-quality content mills can easily replace those writers with GPT-3-powered tools.
Although we strongly discourage businesses and brands from removing human beings from the writing process entirely this early on, these tools can save costs for teams.
There is a lot more to SEO copywriting than just generating words. SEO copywriters work hard to match the tone, voice, and style of their brand or the brands they write for, but GPT-3 will continue to get better and detecting and replicating these nuances with their text generation.
#5: GPT-3 is Impacting Search. Big Time.
GPT-3’s direct application to the SEO industry is abundantly clear. No one has monetized machine learning and NLP as well as Google, and it’s been a long time since Google had an equally-matched competitor. The commercial GPT-3 product is changing that.
Advancements in the field of natural language processing are the reason why when you prompt Google with any question or keyword phrase, it understands your intent and finds the web page it believes will best serve your needs. But it is not only Google’s NLP capabilities, but its immense indexing power, that catapulted it to a 92% share of the search engine market.

But because GPT-3 is now a commercial product, it could equip other innovators and brands to develop search engines of their own. The search engine market could finally open up to new competitors who have similar technological advantages and cloud services, like AWS, Microsoft, or Apple.
As the field of natural language processing continues to progress, digital marketers could see entirely new search engines and advertising platforms emerge. GPT-3, and more products like it, could create seismic shifts in the realm of search.
Until then, Google’s role as the market leader is unlikely to change anytime soon.