How to Improve Website Performance for Better Rankings
When it comes to website speed, time is money. A few extra seconds of page load time could have a major impact on your ability to keep visitors, make sales, and boost your conversion rates.
How quickly does your website load for desktop and mobile users? If the answer is more than two or three seconds, you may be losing traffic as visitors bounce back to the search results page and choose a faster-loading page. And the question we can help you answer is how to improve website performance to improve your user experience and Google rankings.
When it comes to website speed for e-commerce websites, time is money. A few extra seconds of page load time could have a major impact on your ability to engage visitors, make sales, and boost your overall conversion rate. However, if you’re looking to boost your site’s speed on searchers’ browsers, you’ve come to the right page. This article will cover how to transform your website’s page load speed from laggy to snappy for a better user experience.

How Website Speed Impacts Your Business and SEO
When it comes to your site’s speed, load time does more than just make your users wait–it affects your site’s ranking, your visitors’ user experience, and more.
Page Load Time is a PageRank Factor
Google is on a mission to make searching the internet a better experience for all. One way they do this is by prioritizing search results page load time is a Google ranking factor that’s become even more prominent with the release of Google’s Core Web Vitals.
This is all to say that a fast site speed is essential if you want your site to rank higher and for more keywords. So, when you improve your website performance, you’re improving your chances of ranking and earning organic traffic.
Long Load Times Lead to Less Revenue
It should be no surprise that the longer the delay in page load time, the more traffic a site will lose. A slow website can result in lost sales opportunities, lost revenue, and lost growth potential. According to Business, 53% of mobile users will exit a page if it takes longer than 3 seconds to load.
Slow page speed also disrupts the user experience, often impacting buying decisions.
Conversely, increasing site speed corresponds to higher conversion rates, increased revenue, and better brand credibility.
Here’s how page speed impacted some best-known, enterprise-level websites:
- Amazon reported a loss in revenue of 1% for every 100 milliseconds of page load delay
- Walmart saw a 2% increase in conversion rate for every second of page speed improvement
- Mozilla increased page load speed by 2.2 seconds and Firefox downloads increased by 15.4% (or 10 million in a year)
- Shopzilla: Decreased load time from 7 to 2 seconds and saw a 50% decrease in their operational budget
Companies of all sizes experience positive business results related to increasing site speed. Even for smaller sites, improving load times needs to be a priority in your search engine optimization (SEO) efforts.
Search Engines Prefer Providing Searchers Fast Websites
Website speed figures significantly into the algorithms used to rank sites in search engine results. The faster your site loads – especially with mobile searches – the better your position in the SERPs.
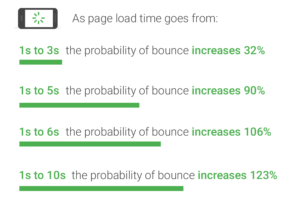
Site load time is part of Google’s search ranking algorithm. And, because of its mobile-first policy, load times on mobile sites now take precedence over desktop systems.
Mobile-First Indexing | WMConf Lightning Talks
What Is an Ideal Load Time According to Google?
Google offers these benchmarks to help site owners set the bar for page speed:
Average speed index (how quickly a mobile page displays to a user): 3 seconds
Average request count (number of content pieces needed to display the entire mobile page): Fewer than 50
Average page weight (total size of a mobile web page in bytes): Less than 500K
And Google’s Core Web Vitals outline optimal load times of the most impact elements as follows:
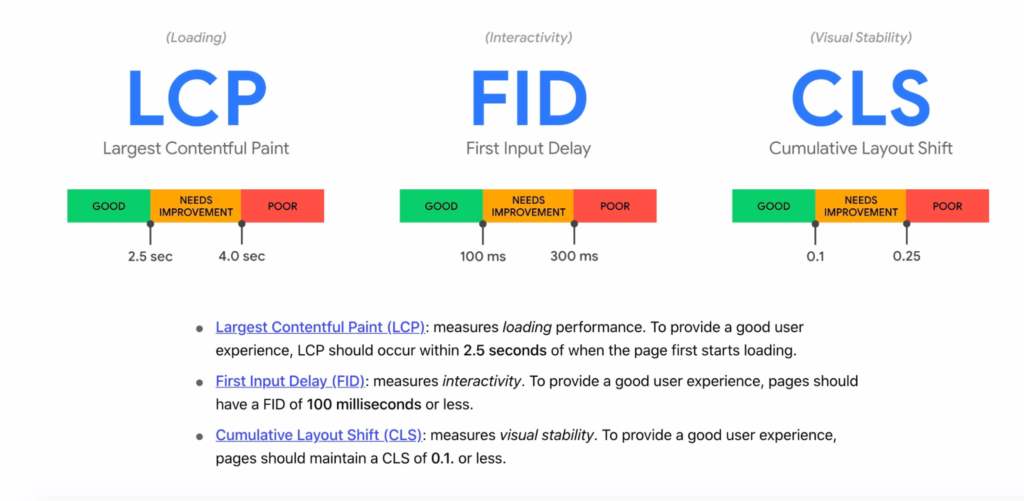
The bottom line is that site speed, SEO, and business growth are interlinked. If your site gets penalized by Google due to page speed issues, your rankings will drop, and so will your page views. Your site could even wind up with a manual penalty and become completely hidden from the SERPs.
This loss of visibility can translate to:
- Lower ad revenue
- Fewer conversions
- Fewer sales
- Poor brand reputation
Improving your site speed is a key business growth strategy that needs your focus now.
How to Improve Your Website Performance on Desktop & Mobile
It’s obvious that page speed matters. But when it comes to speeding up your pages and overall site, it’s often easier said than done. Why? There is not a one-size-fits-all solution to making every site perform at its optimal speed. Furthermore, site owners, web developers, and SEOs all have their individual technical abilities.
However, selecting the most appropriate tactics for your site listed here can help you troubleshoot then fix page speed errors.
1. Test Your Current Website Speed
There are a number of online tools to test how fast your website runs. Free access to PageSpeed Insights allows every site owner to identify any elements that may be slowing their site down.
The Google PageSpeed Insights tool (PSI) is the one most commonly used by website owners. It provides you with a report card and excellent insight into what is slowing your site down. Another magical aspect of using PSI is it provides the same data that Google does. This gives you a peek into how Googlebots will score your speed while indexing.
Keep in mind that your browser and internet connection will affect your PSI score.
How to Use PSI
Simply enter the URL you want to test into the text field and hit Analyze. For the most accurate data, disable any extensions in your browser.
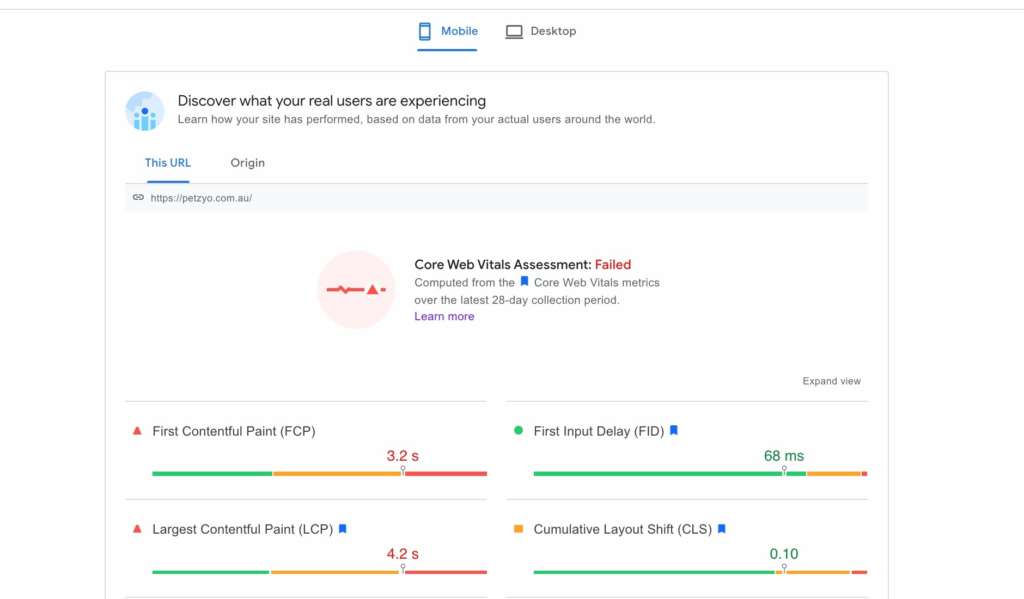
Then, the PSI tool returns a report on your site’s Web Core Vitals for mobile devices. To see your site’s performance on desktop, select the desktop icon at the top of the screen.
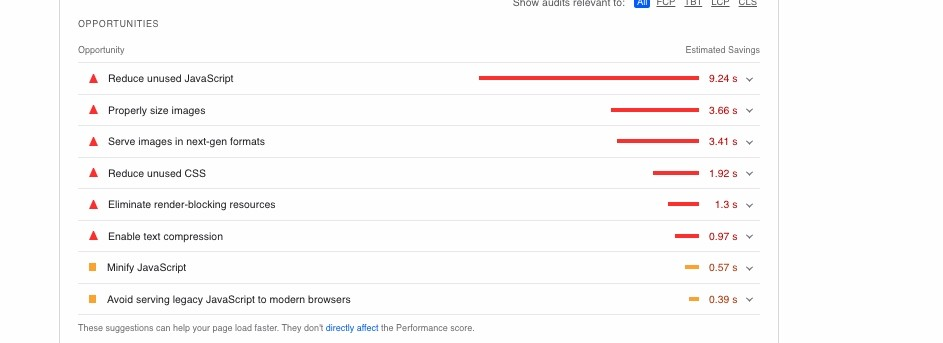
When you scroll down, you will find a speed analysis of your page, including some opportunities that Google suggests. These are recommended ways to improve desktop and mobile page load times.
 Key outputs of a PageSpeed Insights report include:
Key outputs of a PageSpeed Insights report include:
A performance score that summarizes the page’s overall performance.
- 90 or above is “fast”
- between 50 and 90 is “moderate”
- lower than 50 is “slow”
Opportunities for site improvement. Focus on the highest items on the list first. Click the “drop-down arrow to the right of the opportunity item to discover tips on how to fix the identified problem.
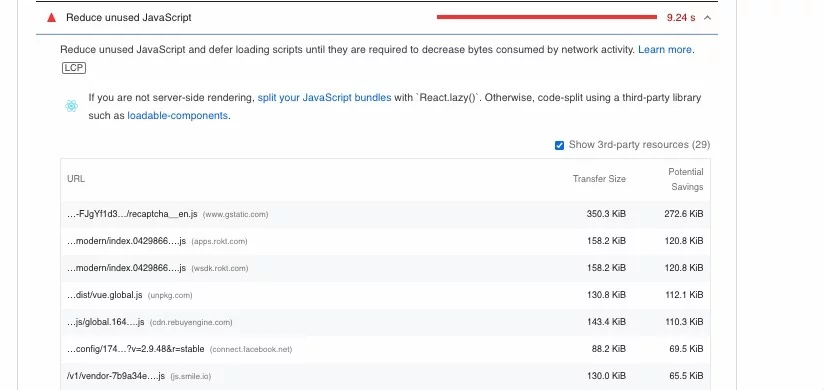
Diagnostics for technical issues. With the same option to expand the item for more details and an explanation as to how to fix it.
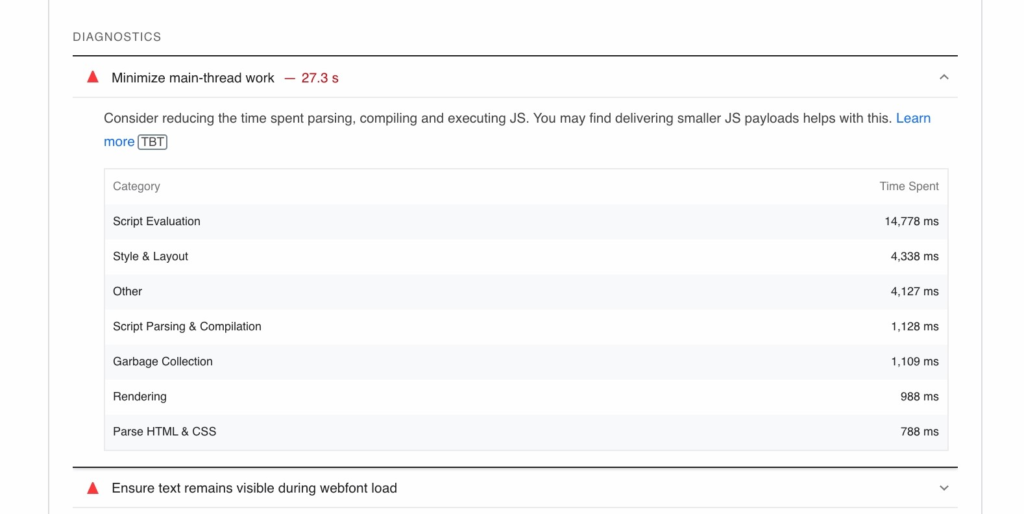
What to Do with Your PSI Data
Evaluation of your site’s Core Web Vitals and other unifying Google quality signals Google experience allows you to prioritize site changes. If you’re tech-savvy, you can fix some of these issues yourself. Otherwise, you may want to consider hiring a web developer for page speed optimization.
If you’re evaluating how to best use your web development budget, perform a URL analysis on your landing pages and popular blogs. Note any overarching themes in your metrics. For example, if your FCP is too high on average, you may have data-rich media above the fold on the majority of your pages.
You can also keep a list of your pages with the lowest performance scores.
2. Consider changing your web host

If you have a shared hosting plan like those on BlueHost, consider switching to a dedicated server or cloud hosting.
Though shared hosting invariably comes with a lower price tag, it can also affect site speed because resources like memory and bandwidth are shared across a number (and sometimes quite a larger number) of websites. Additionally, you can never account for traffic spikes for another site on the server–which will affect the performance of your website.
Switching to a dedicated server or cloud hosting as the sole website owner can increase site speed because resources are no longer being tapped by multiple sites. This is especially important for enterprise-level organizations that have a high bandwidth requirement in order to serve a robust amount of content.
3. Update your website theme
If you use a content management system (CMS) like WordPress, switch to a current WordPress theme that is already optimized for speed. Such themes are light and flexible, and some are focused only on including elements that support search engine optimization best practices.
While you’re making changes to your website, consider removing unnecessary widgets that require a lot of data to load and run.
4. Minimize HTTP requests
HTTP requests, such as 301 redirects, occur when a user first visits your site. They are sent to your server (on your hosting platform), requesting the files needed to render your site on the user’s screen. The more new requests made in order to get all the files needed for your site, the more time that web page will take to load.
What are redirects?
Redirects are code instructions that forward your user from one location on your site to another. When you have a number of requests in a chain, it can take the webserver a lot of time to return the right data to your visitors’ browsers.
One way you can think of redirects is if you’ve asked one of your children to go find a specific book. They arrive at the room where they expect to find the book, but instead, they find a note saying it’s in another room. This detour delays their delivery of the book.
Redirects are commonly used for site migrations, website redesigns, or when content pruning, but each redirect adds to how long it takes for a web page to load.
How to reduce redirects
It’s best to avoid redirects when you can since they’re one of the easiest ways to slow down website performance. But if you do have some, Google advises that you:
- Never require more than one redirect to get to any of your resources; and
- Never link to a page that you know has a redirect on it.
If you have spare time, you can also go through your internal links and revise their URLs to the new URL. You can also request your referral sites do the same.
5. Compress your files
Compressing your site files helps reduce HTTP requests. You may see response time decrease by as much as 70 percent. Gzip is a free tool used by web developers to effectively compress site files and improve how quickly a website loads.
This works exceptionally well for improving website performance for sites with a lot of images.
6. Optimize your images, videos, and other media

Images, videos, and other rich media are often the culprits when it comes to slow loading times. On the other hand, compression is often the easiest way to fix slow media loading times.
Save site images in the smallest possible file size without reducing image quality on the user’s end. Some recommendations for optimizing images include:
- Using JPEG or .jpg format for colorful images, PNG for simple images, and GIF for animated images.
- Reducing file dimensions to a suitable size that is visible and clear on multiple devices
- Using an image compression tool like TinyPNG or JPEG Mini to compress images.
You should also use lazy loading for any images or larger elements below the fold. Lazy loading speeds up the amount of time it takes the most important elements to render. Additionally, it also reduces the number of HTTP requests. It works by utilizing the initial bandwidth to prioritize elements visitors will see first.
7. Consider using a content delivery network (CDN)
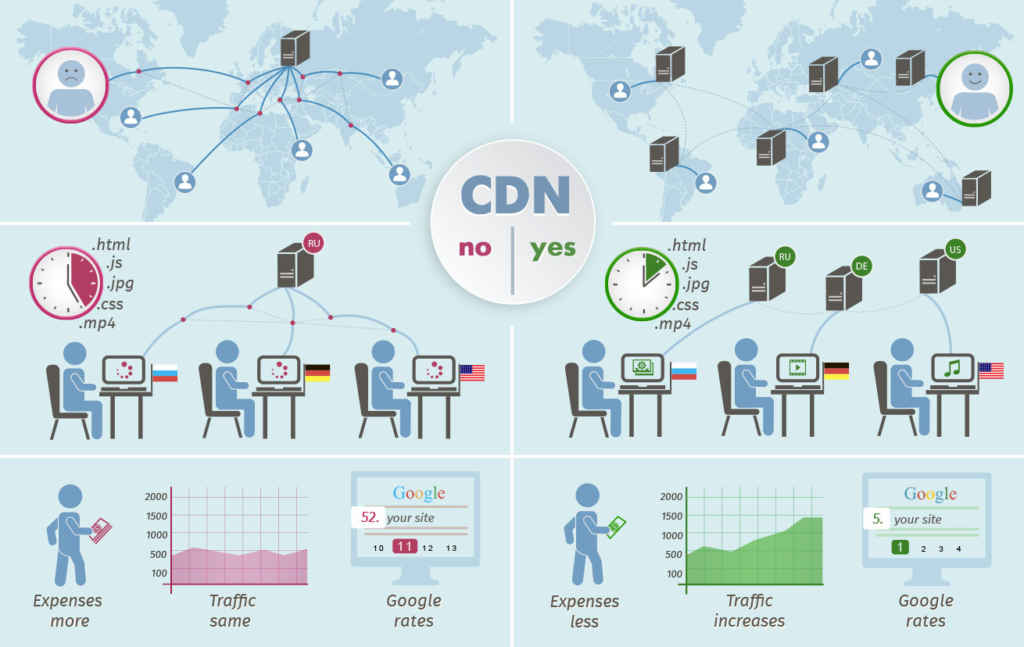
In today’s digital world we often do not think about data traveling through physical distance, but it does. A CDN is a network in close geographic proximity to your web server that delivers content.
Close proximity decreases transmission time, which can improve the user experience by increasing the speed and site performance of desktop and mobile sites.
For example, if your site servers users in Florida, your CDN should be located within the US, and ideally close to Florida. This will reduce the page load times since the data for the server request can return to the browser with stealth speed.
8. Check your plugins
Each plugin you have on your site shaves time off your webpage rendering speed. This is especially common for WordPress sites.
Luckily the fix is easy. Review your plugins and ditch the ones you don’t use. If better-optimized plugins can replace the ones you want to keep, make the switch.
9. Clean up your site
Minification or the process of removing unnecessary and redundant data can do wonders for your website’s performance. This process is a way to clean up any excessive code that is bogging down your javascript (JS), HTML, or CSS files. This can increase your site’s responsiveness instantly.
Minification
To begin our minification, you will need to view your website’s code. You can do this in the element inspection menu in Chrome by pressing CTRL + i or right-clicking on the page and selecting Inspect. If you notice a lot of spaces, there’s a good chance minification can make the webpage faster.
You will then want to use the HTML editor if you have a WordPress website to pare back on excess lines of code. If you’re unfamiliar with working on CSS files, Javascript files, and HTML, you can always ask your web developer or use an agency as a resource.
The Trade-Off
Of course, there’s a slight tradeoff with minification. Longer HTML files, javascript files, and other code are often easier for developers to navigate.
Other ways you can clean up your site include:
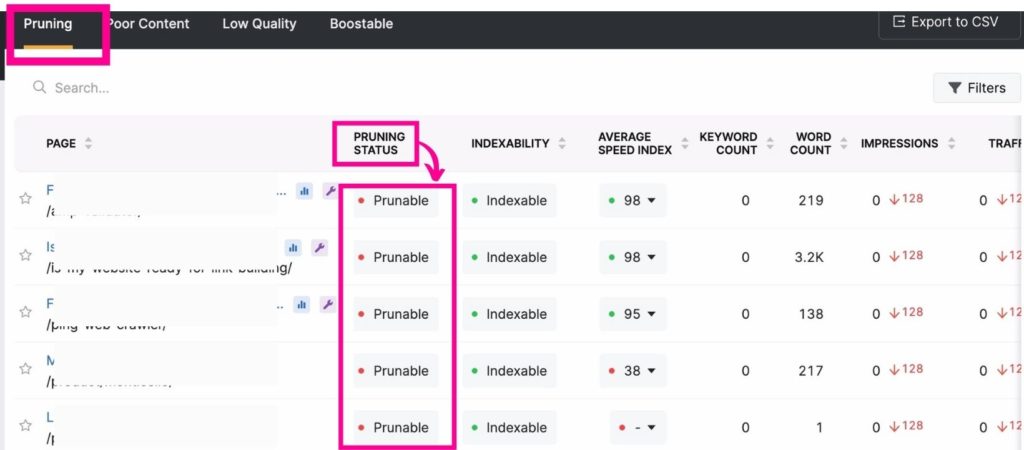
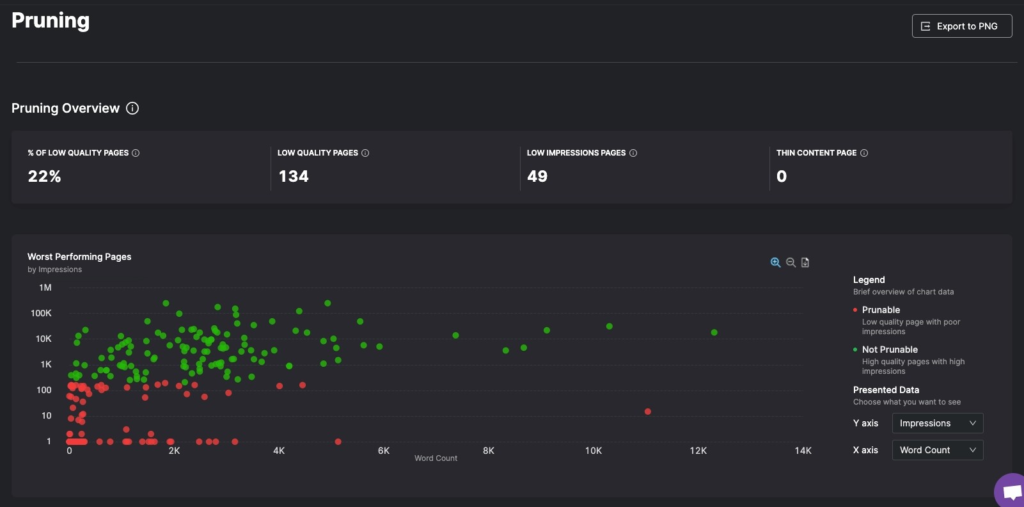
Pruning outdated content, pages, and files. Search Atlas’s GSC Insights and Site Audit tools provide you with a list of sites that are underperforming and those that are at risk of keyword cannibalization.
Additionally, fix or remove broken links to boost how fast your website loads
10. Enable browser caching
Every users’ browser has a cache. Within the cache is data from the version of your site the user last explored. When a browser is called upon again to load the same site, the browser will reach into its cache and retrieve the previous data, or static files, to display.
By enabling browsers, such as Chrome to store your site’s static files, you’re improving your page speed metrics and providing a better user experience.
This tactic is huge a benefit for returning visitors. This can cut down the amount of time a page loads by nearly 100%!
11. Optimizing Your Website’s Fonts
While it may seem inconsequential, the font you choose for your site does affect page load speed. When you use a bespoke font (or web font) for branding purposes, you could be detracting from your website’s performance. Here’s how:
System fonts, such as Arial, Calibri, and Times New Roman do not require any data to be fetched from the server or elsewhere on the internet. They’re already stored in the user’s computer or mobile device.
Web fonts, on the other hand, require the visitor’s browser to wait for the data for the font to be fetched from the server. And this is the best-case scenario. Sometimes, web fonts require the data to be fetched from another webpage, which can result in high load time increases and a poor user experience.
Choosing a font from Google Fonts allows your website to optimize for speed without sacrificing style.
12. Give Your Header a Boost

An attractive, easy-to-navigate site is a must for e-commerce. This is where your header often earns its keep. However, it’s important to keep in mind that your header will load above the fold on every one of your web pages. Luckily there are some tricks to ensuring your header isn’t slowing down your page load speed.
- Load your JS scripts last
- How CSS files to your footer and combine into a single CSS file
- (Again) delete unnecessary plugins
- Optimize your fonts (see above)
SEO Software for Page Speed
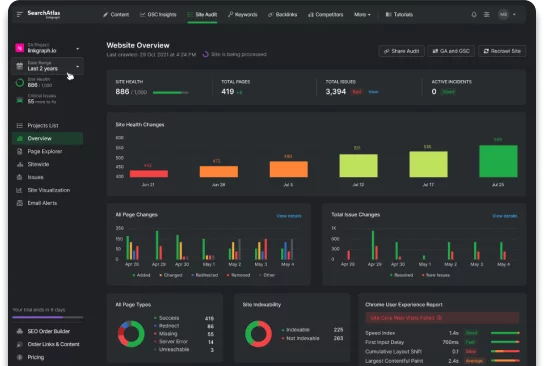
As you likely know, when you optimize for speed, you will need to plan for a multi-faceted approach. This can be quite a large investment of time and juggling different platforms such as Google Analytics, GSC, and Google Webmaster tools. However, if you would like to save time and keep your speed optimization and other SEO tasks in one place, we recommend using software like Search Atlas.
Search Atlas allows you to track the overall performance of your website with a single sign-in. Because it’s built over Google’s API, users receive daily updates on their website’s SEO metrics, including page load speed.
Here’s a closer look at the analytics Search Atlas provides
Monitor your website speed, including mobile devices on a regular basis with the Site Audit tool. Other features of this tool include:
- Page Speed: View page load speed data for mobile devices and desktop. See how your site compares to the average user experience and how many of your pages need speed optimization.
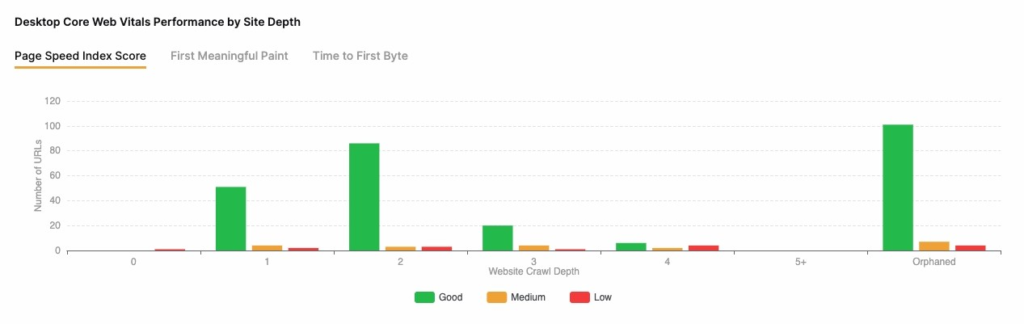
- Redirect reports: identify pages with redirects in order to decrease server response time.
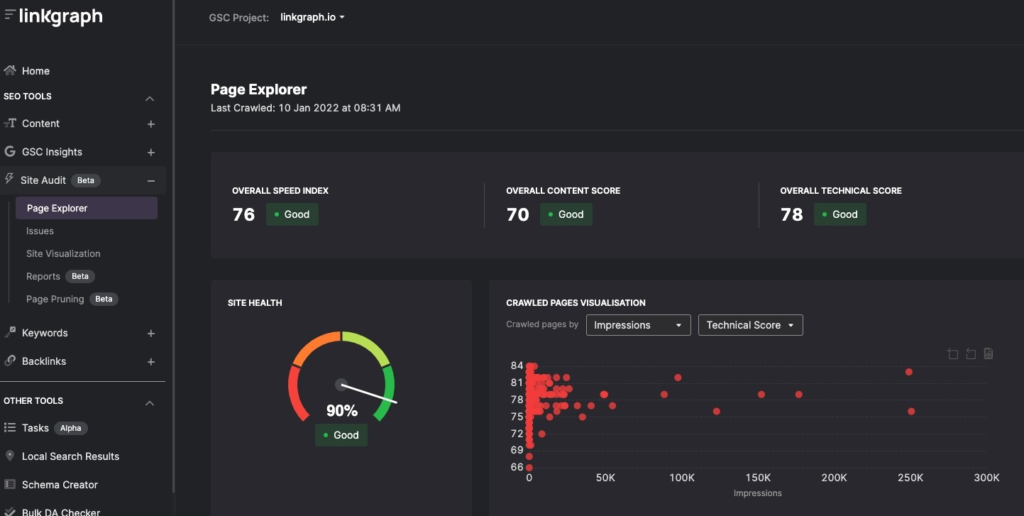
- Overall Index Speed: View your website’s performance through the eye’s of Google’s crawlers
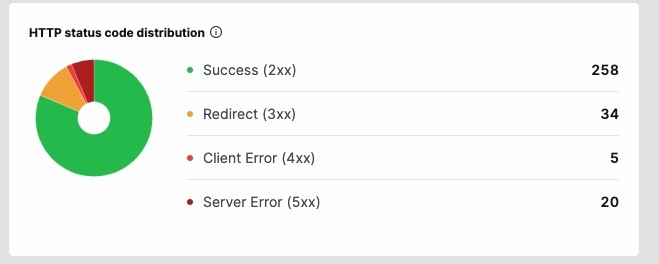
- HTTP Status Codes Distribution: Identify if switching servers will improve page speed
- Content Duplicates: Streamline site-wide content clean up with duplicate identifier
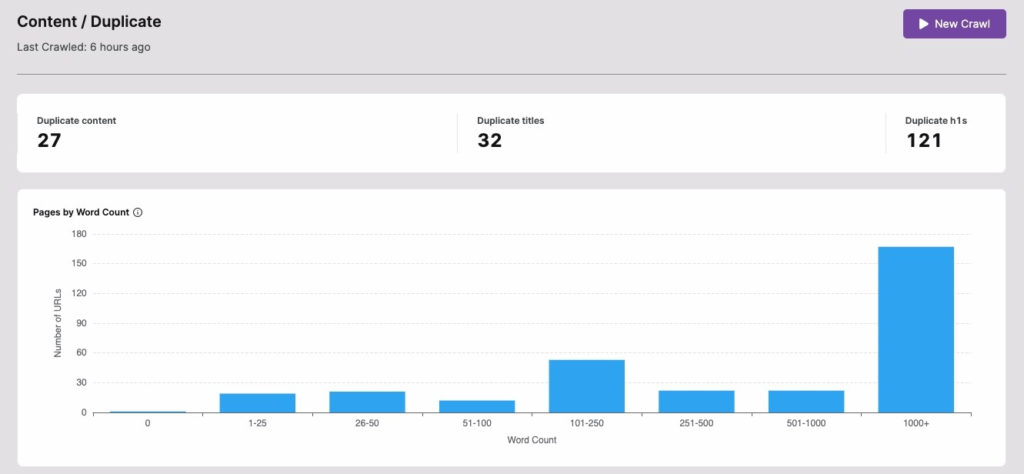
- Page Pruning: Reduce unnecessary URLs and strategically keep only those that are Boostable.
Free Page Load Speed Monitoring Options
At a minimum, track your desktop and mobile search ranking results, and check your PSI score if you see your site rankings lower on the SERPs.
You can use these steps to make continuous speed improvements:
- Use your initial speed test as your baseline metric and test current speed on mobile and desktop devices.
- Check Google PageSpeed Insights suggestions for recommended improvements.
- Based on your results and PSI recommendations, decide which tactics to use to improve the speed of your desktop and mobile site.
- Retest your page speed after completing each tactic to assess results.
Rinse and repeat as often as necessary to keep improving your page speed.
Improve Your Website’s Performance & Speed for Better Rankings
Whether you own an e-commerce website, make money off of ad revenue, or simply host a forum as a hobby, you want your page load speeds to be swift and seamless. We predict Google will continue to emphasize the importance of page speed as a ranking factor for search queries. So, begin optimizing your site for good page load time. While this requires revising a lot of factors, you can start the process by prioritizing the most pressing tasks or knocking out those that are easy fixes.
Consider using lazy load images, eliminate plugins that don’t serve your site speed, switch to loading your js files last, and enable website caching. Other quick fixes can include switching your WordPress theme, using a minification tool, and investing in your own server or a CDN.
Remember to set benchmarks and when you decide how to improve your website performance analytics. Then use a tool such as Search Atlas which pulls data directly from Google Search Console.