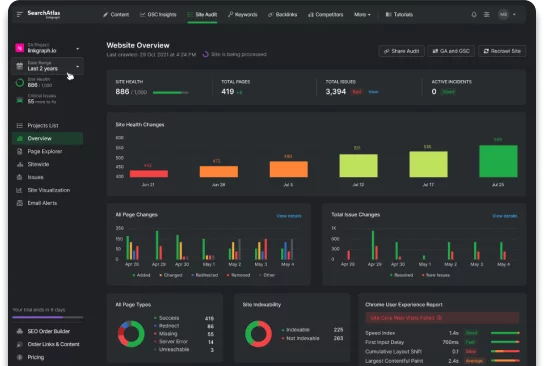
SEO and Article: Semantic HTML Element
Optimizing Your Content With Semantic HTML Elements for Better SEO In the ever-evolving landscape of SEO, the significance of semantic HTML elements is frequently underestimated. A well-crafted […]
Optimizing Your Content With Semantic HTML Elements for Better SEO
In the ever-evolving landscape of SEO, the significance of semantic HTML elements is frequently underestimated.
A well-crafted semantic structure ensures that a website’s content is not only accessible to users but also to search engines, paving the way for an enhanced understanding of page content.
By incorporating semantic HTML tags, web developers grant search engines like Google clearer insights into the relevance and context of web pages, ultimately influencing search rankings.
These markers serve as guideposts that lead crawlers through the content, signifying the importance of paragraphs, headings, and other content areas.
Keep reading to discover how mastering semantic HTML can revolutionize your site’s SEO performance and user accessibility.
Key Takeaways
- Semantic HTML Elements Like ,
- Misusing Semantic HTML Can Confuse Both Users and Search Engines, Leading to Poorer SEO Outcomes and Navigability Issues
- Incorporating Semantic HTML Elements Is Critical for Enhancing on-Page SEO and User Navigation, Aiding Indexing, and Increasing Local Search Presence
- LinkGraph’s SEO Services Harmonize Technical SEO Expertise With HTML5 Semantics to Ensure Content Is Indexable and Discoverable by Search Engines
- Advanced SEO Techniques, Including Structured Data With Schema.org and Microdata, Enrich a Website’s Presence and Interaction on Search Engine Results Pages
Understanding the Role of Semantic HTML in SEO

There exists a nuanced interplay between Semantic HTML elements and its influence on search engine optimization (SEO), a dynamic that web developers and content creators must adeptly navigate to enhance online visibility.
Semantic HTML, by imbuing web content with intrinsic meaning, facilitates a richer interpretation by search engines, propelling a website’s relevancy within the vastness of search results.
This introductory discussion aims to elucidate the essence of Semantic HTML, dissecting its profound SEO impact and examining how search engines harness semantic markup to decipher and rank the labyrinth of online information, ultimately fortifying the connection between content semantics and search relevancy.
Explaining Semantic HTML and Its Impact on SEO
The term ‘Semantic HTML’ refers to the convention of utilizing HTML tags that explicitly convey the meaning and structure of the web content they encase. These discernible elements, such as ,
Adoption of Semantic HTML is a fundamental aspect of an SEO content strategy, as it improves the clarity with which machines, including web crawlers and screen readers, interpret page content. When a website’s markup is semantically rich, it not only reinforces the content’s context and relevance for user queries but also enhances the comprehensiveness of search engines’ indexing processes, paving the way for improved SEO performance and higher search visibility.
How Search Engines Use Semantic Markup
Search engines utilize semantic markup to streamline the categorization and retrieval of web content. This systematic approach helps them to quickly discern the context and relevance of text within HTML elements, such as headings, paragraphs, and sections, enhancing the user’s search experience by delivering content that precisely matches their search intent.
The strategic application of semantic HTML tags, like and , provides search engines with a structured framework they can use to interpret the varying content areas of a web page. The utilization of these tags leads to a more accurate understanding of page semantics, directly influencing how search engines rank and present web pages to users:
| HTML Element | Description | SEO Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| <header> | Defines introductory content or a group of navigational links. | Serves as a relevance signal for search engines, emphasizing the overall topic of the web page. |
| <nav> | Represents a section with navigation links to other pages or parts within the website. | Aids search engines in understanding site structure and the hierarchical value of content. |
| <main> | Encapsulates the dominant content of the body of a document or application. | Highlights the primary content area, which holds significant weight for indexing and ranking. |
| <article> | Denotes a self-contained composition in a document that is independently distributable or reusable. | Signals to search engines the boundaries of thematically cohesive content, often crucial for page ranking. |
| <aside> | Indicates content tangentially related to the content around the element. | Gives context for sidebars or supplementary content, clarifying non-primary information for search algorithms. |
| <footer> | Represents the closing content of a web page, typically containing information like copyright and contact details. | Assists search engines in identifying ancillary yet pertinent details that may not be central to the main content. |
The Relation Between Semantic HTML and Relevancy
In the digital realm, relevance equates to visibility. Utilizing Semantic HTML effectively heightens a web page’s relevance, signaling to search engines the core themes presented, thus permitting a more targeted presentation of search results aligned with user queries.
Search engines attribute high value to content coherence when ranking web pages. By demarcating content through Semantic HTML, developers and SEO strategists provide a clear map for search engines to correlate user intent with the most pertinent content, thereby enhancing visibility and user satisfaction.
Mastering Semantic HTML Tags for Improved SEO

Embracing the power of semantic HTML tags can transform the impact of a website’s SEO, establishing a foundation upon which content is not only rich in meaning but also primed for search engine rankings.
As webmasters identify and integrate core semantic elements into their digital strategy, they unlock the potential for heightened clarity and accessibility of their content to search crawlers.
This subsection will explore essential practices to enhance one’s SEO strategy through semantic tags, common pitfalls to avoid in their implementation, and the substantiated benefits that accompany the meticulous structuring of web content using proven HTML conventions.
Identifying Core Semantic HTML Elements
Identifying core Semantic HTML elements is critical for refining a content strategy focused on SEO. Web developers and SEO professionals prioritize these elements to provide clear structure and relevance to their page content, directly influencing how machines, including web crawlers, process and evaluate the information presented.
Among these elements, the
| HTML Element | Functionality |
|---|---|
| <header> | Delineates the top section of a web page, usually containing the title and main navigation links. |
| <nav> | Defines navigation links to facilitate user and search engine movement through the site. |
| <article> | Encases a self-contained composition, enhancing the indexing of standalone content blocks. |
| <footer> | Identifies the bottom section of a page, providing additional but significant information such as copyright notices. |
Incorporating Semantic Tags Into Your Content Strategy
Incorporation of semantic tags is a strategic move that enhances content strategy, equipping web pages with discernible roadmaps for Search Engine Crawlers. Webmasters can elevate the significance of their content in the eyes of search engines by embedding semantic elements that highlight primary subject matter and delineate supporting information, thus bolstering SEO efforts and user experience.
By weaving semantic HTML tags throughout web content, SEO professionals are able to draw clear boundaries between different content types, enabling a more organized, accessible, and indexable web page. This practice not only clarifies the site’s content hierarchy for search engines but also helps match user queries with the most relevant information, ensuring a congruent search and discovery process.
Mistakes to Avoid When Using Semantic Tags
Misapplication of Semantic HTML can inadvertently obscure the intended hierarchy and dilute the potency of content strategy. Overusing elements such as and can lead to a convoluted structure that confuses both users and search engines, ultimately undermining a site’s SEO impact and navigability.
Equally critical is avoiding the disregard of Semantic HTML’s syntax and accessibility principles. Neglecting to use header tags correctly, or opting for non-semantic markup due to expedience, can severely impede web crawlers’ understanding of content significance, leading to suboptimal search rankings and poor user experiences.
Structuring Your Content With Semantic HTML5

In an era where every nuance of web design can tip the scales of search engine rankings, employing a well-crafted page layout rooted in Semantic HTML5 is not a fleeting trend but a cornerstone of a robust SEO strategy.
As such, web designers and content strategists must possess a deep understanding of semantic tags—optimizing the digital foundation of headers, footers, and section elements to bolster discoverability and enhance content visibility.
This initiation into Semantic HTML5’s layout principles will pave the way for content that is not only user-friendly but also meticulously aligned with the intricate algorithms of search engines.
Outlining a Semantic HTML5-Based Page Layout
To optimize the layout of a webpage using Semantic HTML5, web developers must meticulously position elements in a way that emphasizes the underlying structure and theme. Establishing a well-defined layout with the
An effective Semantic HTML5 layout functions as a blueprint for Search Engine Algorithms to accurately assess and index a page’s content for optimal visibility:
| HTML5 Element | Placement Within Layout | Contribution to SEO |
|---|---|---|
| <header> | Top of the page | Sets the page’s thematic stage, aiding search engines in contextual understanding. |
| <nav> | Following the header, or within | Improves site navigation clarity, supporting search engine site mapping. |
| <main> | Central part of the body | Signifies primary content, pivotal for indexing priority and user engagement. |
| <article> | Within main, encapsulating independent content | Demarcates significant content blocks, often enhancing content’s ranking potential. |
| <section> | Under main, to group thematically similar content | Clarifies content subdivisions, which assists in finer-grained topical relevance assessment. |
| <aside> | Adjacent to main content areas | Identifies secondary content, informing search engines of auxiliary topics. |
| <footer> | Bottom of the page | Houses meta-information and additional links, solidifying the page’s comprehensive context. |
Best Practices for Using Header, Footer, and Section Tags
Implementing header, footer, and section tags appropriately goes beyond mere placement within an HTML document; it demands a strategic approach that aligns with search engine optimization best practices. Headers should encapsulate the core theme of the content, footers ought to offer supplementary but essential information, and section tags must systematically delineate related content, thus cultivating an SEO-friendly architecture.
Integrating these elements with a clear understanding of their functional distinctions enhances a website’s searchability and user navigation. The deliberate use of header tags conveys topical dominance to search engines, while footers and sections serve to enrich semantic depth and structure, optimizing the meticulous crawl and indexation processes of search algorithms:
| Element | Functional Distinction | SEO Optimization Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| <header> | Introduces the primary subject matter and navigational context of the content. | Reinforces content’s topical emphasis, guiding the search engine’s comprehension of main theme. |
| <footer> | Delivers additional insights and links that frame the content body. | Supplies contextual layers, rendering a comprehensive overview for algorithmic assessment. |
| <section> | Segments thematically related material within a document. | Introduces clarity to content groupings, facilitating nuanced relevance evaluation for ranking. |
Enhancing Content Discoverability With Proper HTML5 Structure
Expertly crafted HTML5 structure serves as a beacon to search engines, signifying a webpage that merits attention and stands as a source of authoritative information. Web creators implement semantic tags such as , , and to carve out distinct content areas, thereby streamlining the pathway for search algorithms to latch onto and elevate the most germane material in response to user queries.
The marriage of technical SEO prowess and HTML5’s semantic precision creates a vault of content that is readily discoverable and indexable by search engines. By using semantic elements thoughtfully, LinkGraph’s SEO Services ensure that each segment of content is efficiently categorized under its relevant context—a factor that is known to markedly boost a page’s visibility and rank in the digital ecosystem.
Leverage Semantic Elements to Boost on-Page SEO

Professionally sculpted content is the linchpin of an effective on-page SEO strategy, where understanding the nuanced utility of semantic HTML elements becomes paramount.
Astutely incorporating tags such as and can amplify the clarity of main and supporting content, ensuring precise indexing and enhancing topical relevance.
Likewise, the deliberate utilization of navigational
Furthermore, the optimization of multimedia through tags like and complements the intricacies of a content strategy, beckoning a website’s climb up the search engine ladder.
This section unfolds the transformative potential of such semantic tags in refining the framework of your web content for augmented SEO impact.
Using Article and Aside Tags for Main and Supporting Content
Effective on-page SEO requires a refined approach to assigning semantic significance within a web page. Utilizing the tag, LinkGraph’s SEO services can signal the importance of primary content to search engines, delineating each substantive piece as a standalone entity that deserves recognition and weight in search rankings.
Conversely, the strategic deployment of the tag allows for the distinction of supporting content, such as related topics or supplementary data, which is pivotal in creating a complete picture for search engines and users alike. This clear demarcation empowers search algorithms to parse and prioritize content accurately, reinforcing the efficacy of a website’s SEO framework.
The Importance of Nav and Address Elements for SEO
In the realm of on-page SEO, the significance of properly employed
Implementing these HTML elements strategically enhances a website’s SEO by delineating a pathway for search engines to follow, effectively mapping the site’s content and geographic relevance. As a result, websites experience improved indexing and higher credibility in the eyes of search algorithms, thereby increasing the potential for better search rankings:
- Ease of navigation with
- The tag fortifies local SEO by delivering precise business location details to search engines.
- Strategically structured semantic elements synergize to elevate a site’s usability and SEO performance.
Optimizing Media Elements With Figcaption and Picture Tags
The integration of and tags is an astute refinement within the media-rich landscape of modern web pages. These elements not only reinforce the descriptive data of visual media for search engines, but they also enhance user accessibility, creating a synchronized environment for humans and machines alike.
Media optimization is essential for on-page SEO, and LinkGraph’s SEO services adeptly employ to provide context for images, while the tag allows for responsive image selection suited to various devices, directly influencing user engagement metrics:
- The element enhances image relevancy through descriptiveness, encouraging better indexing of visual content.
- Utilizing the tag aids in delivering optimal image versions for different screen sizes, which can improve page load speed and user experience.
- Properly labeled media facilitates accessibility, ensuring content fulfills usability standards and SEO best practices.
Boosting Accessibility With Semantic HTML for Better SEO

Advancing accessibility through Semantic HTML is a pivotal component in refining a website’s alignment with search engines’ evolving algorithms.
The imperative to foster accessible content unfolds a dual benefit: it aids those utilizing assistive technologies while simultaneously boosting a page’s SEO credentials.
By integrating ARIA roles and landmarks, web developers can go beyond mere compliance, elevating the user experience for a wider audience and improving the site’s discoverability.
This enhancement underscores the symbiotic relationship between accessibility measures and SEO success—where accessible design principles intersect with the meticulous demands of search engines, there lies a potent avenue for increasing online visibility and user engagement.
How Accessibility Improves SEO Through Semantic HTML
Embedding Semantic HTML into web page designs inherently enhances the overall accessibility, which, in turn, supplements a website’s SEO performance. By crafting content that is naturally easier for search engines to interpret through structured data, such as ARIA landmarks and roles, web developers enhance the navigability for both assistive technologies and search engine crawlers, thereby magnifying a site’s visibility and rank.
Careful implementation of Semantic HTML elements not only serves the needs of those with disabilities but also strengthens the context and readability of content for search algorithms. This alignment between user accessibility and search engine guidelines ensures content is optimally formatted, leading to a discernible improvement in a website’s SEO landscape, as search engines reward sites offering a superior user experience.
Creating Accessible Web Content With ARIA Roles and Landmarks
The deployment of Accessible Rich Internet Applications (ARIA) roles and landmarks plays an integral part in creating web content that transcends baseline accessibility. This structured approach lays out clear navigation pathways within web content, allowing persons with disabilities to interact and navigate with ease and precision.
Integrating ARIA roles and landmarks, LinkGraph’s SEO content strategy takes into account the nuances of a diverse user base, streamlining the interaction for assistive technology users. This practice ensures web content is not only reachable by a broader audience but also more intelligible to search engine crawlers, enhancing the SEO footprint of websites that prioritize accessibility.
Using Microdata and Schema for Enhanced Search Results
In the quest to secure a prominent position on search engine results pages, webmasters and SEO strategists recognize the significance of not only employing Semantic HTML but also enhancing it with Microdata and Schema.org vocabulary.
This fusion elevates content clarity for search algorithms, allowing for the generation of rich snippets and improving click-through rates.
This subsection delves into the integration of Microdata with semantic elements and unpacks the transformative merits Schema.org brings to the digital stage, underlining how these advanced SEO techniques enrich a website’s search engine presence and user interaction.
Integrating Microdata With Semantic HTML for Rich Snippets
Mastering the integration of Microdata with Semantic HTML is a decisive step for web professionals keen on magnifying their SEO efforts. This strategic blend enables the crafting of rich snippets—detailed information chunks that search engines can display directly in search results, thus heightening visibility and fostering user engagement.
LinkGraph’s SEO services expertly merge Microdata annotations with Semantic HTML elements, ensuring that a website’s offering leaps out amidst the sea of search results. The nuanced application of these detailed schemas clarifies the content’s context for search engines, which consequently can lead to a better positioning and differentiation in SERPs, inviting increased click-through rates from potential visitors.
The Benefits of Schema.org Vocabulary in Semantic SEO
Schema.org vocabulary acts as a catalyst in sharpening the semantic precision of a website’s content for SEO. By embedding this Structured Data Framework, LinkGraph’s SEO services can articulate content attributes more explicitly to search engines, fostering a nuanced understanding that aligns with user search queries.
The use of Schema.org facilitates the creation of rich, informative search results that do more than merely list a website’s presence; they subtly hint at the content’s essence before a user clicks through. This enhanced visibility not only improves click-through rates but also positions a brand as an authority in its niche:
- Schema.org vocabulary equips search engines with detailed insights, refining query-result relevance.
- Rich snippets fashioned from Schema markup offer a competitive edge in search engine results pages (SERPs).
- LinkGraph’s integration of structured data bolsters the chances of content being featured in knowledge graphs and other search engine enhancements.
The Future of SEO: Evolving Standards in Semantic HTML

As the digital landscape continues to evolve, staying current with the latest Semantic HTML and SEO practices becomes critical for maintaining and improving search engine rankings.
Developing a keen understanding of emerging standards is paramount for content creators and SEO experts who aspire to meet the sophisticated demands of voice search and AI technologies.
Innovations in HTML tags and algorithms necessitate agile adaptation to ensure that content remains optimized for both traditional search queries and the progressive realms of voice recognition and machine learning.
This adaptation lays the groundwork for successful communication with search engines, providing a pivotal edge in a competitive marketplace.
Staying Ahead With Emerging Semantic HTML and SEO Practices
Grappling with the rapid advancements in search technology, experts continually refine their SEO tactics, ensuring their mastery over the interplay of Semantic HTML and emerging search engine algorithms. LinkGraph’s SEO services remain at the forefront, judiciously employing semantic precision in HTML5 to communicate with next-generation search tools and maintain a competitive edge.
Anticipating the shifts instigated by AI and voice search innovation, LinkGraph epitomizes adaptability, pioneering the integration of cutting-edge semantic markers. By advancing their SEO services with an acute focus on future-proofing content, LinkGraph champions the strategic evolution of SEO practices to align with the transformative tide of search technology.
Preparing Your Content for Voice Search and AI Using Semantic HTML
Preparing content for the nuances of voice search and AI demands meticulous semantic structuring that enables these intelligent systems to parse and comprehend page information with astounding accuracy. LinkGraph’s SEO services advocate the implementation of semantic HTML to cater to voice search algorithms, harnessing tags such as
The harmonic blend of semantic HTML elements and AI-friendly content is a testament to LinkGraph’s proactive approach in optimizing digital properties for the future of search technology. By refining web pages with semantic cues delineated through HTML5, LinkGraph bolsters the readiness of content to engage with voice search and AI, driving relevance and readability in the era of sophisticated search interactions.
Conclusion
Optimizing your content with Semantic HTML elements is essential for improving SEO.
Proper use of tags like ,
Incorporating ARIA roles and Schema.org vocabulary can further enhance content clarity and enable rich snippets, improving visibility and user engagement.
As search technology advances, keeping pace with Semantic HTML standards ensures your content remains optimized for the latest developments, including voice search and AI.
Therefore, leveraging Semantic HTML is critical for boosting SEO and future-proofing your content in the digital landscape.