SEO Glossary
350+ SEO terms and phrases with easy to understand definitions.
Search engine optimization comes with a vocabulary of its own. You can learn the skills you need to optimize your website, and this SEO glossary can help you along the way.
We’ve defined the foundational SEO terminology along with more technical terms, so you have a resource you can use throughout your SEO journey. From web page meta tags to search results metrics and search engine crawler jargon, this glossary defines SEO words with straightforward language. We also provide you with examples and links to resources to help you better understand how these terms and phrases fit into your SEO strategy.
Unsure of which section the SEO words you’re unfamiliar with will be in? You can expand the Table of Contents by clicking on the section heading or use the Ctrl+f function (or Command+f for Mac) and type the word you’re looking up.

General SEO Terminology
Within this introductory section, you will find the vocabulary you will need to optimize for local search (like a local SEO glossary), including Google My Business and voice search phrases.
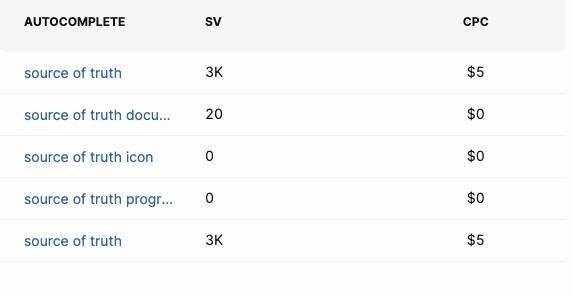
Autocomplete
A feature in Google and other applications that predicts the rest of the word or search phrase based on previous searches. In the Search Atlas Keyword Researcher, this category allows you to better select keywords as well as plan your content.
Browser
An application or program (software) that uses the internet and accesses and displays webpages.
Caching
The action of when a computer or software stores or collecting temporary data to make loading the same data in the future more efficient.
Competition Analysis
Strategically looking at your competitors’ strengths and weaknesses.
Content Scraping
Related Terms: Data Scraping
The illicit practice of stealing original content from a website and posting it to another website. The content is taken without permission and often without attribution. Scraping can be performed manually by copy-and-pasting or automated through bots.
Conversion Rate Optimization
Also Known As: CRO
Strategically making changes to a website or mobile app in an effort to increase conversions (this can include sales, lead gathering, and downloads). CRO often uses A/B tests and comparing the results in order to implement successful methods.
Data
Information gathered for the purpose of analysis or the ‘pieces’ of information transferred from one source to another on the internet. For example, pixels are the data that make up an image on a webpage.
Direct Traffic
A web page users who navigate directly to a web page by typing the URL into the browser (as opposed to navigating to the web page via a referring website).
Domain
A site’s address that translates to a numeric address that is located on the internet. This is the primary aspect of a URL.
Domain Name
A domain name is the address of a specific website. It is what will be typed in for users to reach your website directly. An excellent way to think of your domain name is as a nickname for your IP address. The internet is a vast connection of computers, each one identifying the other with an IP address. IP addresses are numerical sets that can be difficult to memorize. The domain name was created so internet users can enter “twitter.com” instead of a string of numbers.
E-A-T
Expertise, authoritativeness, and trustworthiness: the foundational qualities that Google using to rank businesses, as reflected in Google’s guidelines.
External Link
A link that points outside of the website it appears on. For example, if a link on LinkGraph’s blog links to Google’s web developer website, it would be considered an external link.
Featured Snippet
A preview or answer to a searcher’s question that appears at the top of the SERPs.
Gateway Page
Related Terms: Doorway Page
A page that ranks high in the SERPs for targeted search phrase, but it redirects the user to a new page that does not fulfill the searcher’s intent or provide valuable information. Some gateway pages act as a collection of links to commercial sites.
The most popular search engine worldwide. In addition to its search engine, Google now includes a wide array of sub-softwares and tools. 90% of internet searches are made on Google.
Google Ads
Also Known As: Google Adwords
Google Ads is a paid service provided by Google for advertisers and digital marketers. Google Ads is used to promote content, a website, or a brand through Google searches. It operates by using keywords to generate traffic and leads. Google Adwords advertising can be targeted locally, nationally, or internationally depending on the needs of the business. This service was previously called “Google Adwords.
Google Adwords
See Google Ads
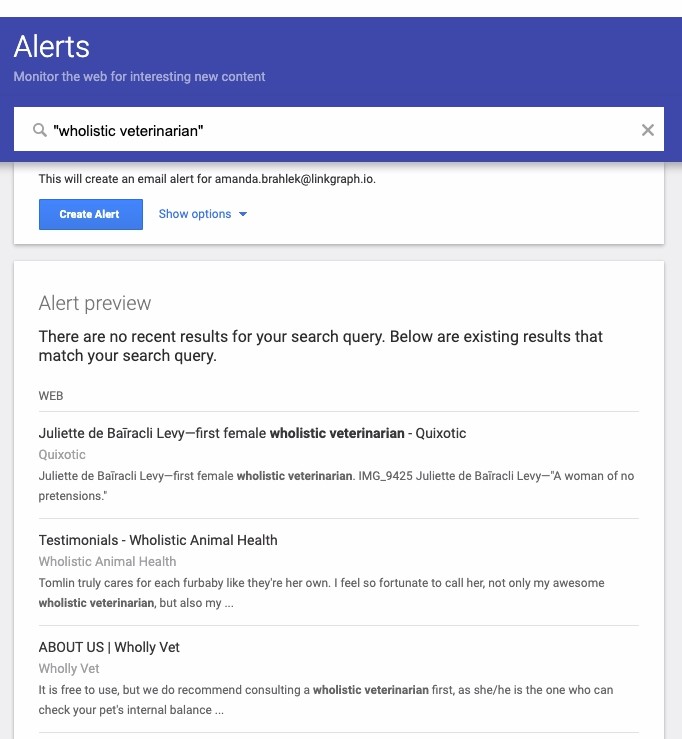
Google Alerts
A setting you can enable for your Google profile so that you will receive notifications of new content for specific keywords.
Google Algorithm Update
A change to Google’s search engine designed to improve search results.
Google Analytics
A free platform made by Google designed to help website owners track and monitor traffic to their website.
Google Auto Complete
Suggested search terms that auto-populate when a searcher begins entering search terms.
Google Bomb
Related Terms: Googlewashing, Search Engine Bomb
A black-hat SEO practice that promotes an irrelevant or low-quality website through the use of a large volume of backlinks. One example of this was a Google bombing that pulled up the band Creed when users searched “worst band in the world.”
Google Fred
A Google algorithm update that rolled out in March 2017 which was designed to de-rank websites using black hat SEO tactics to promote themselves in the SERPs.
Google Hummingbird
A Google algorithm update designed to provide better search results based on users’ intent or sarch goal. This algorithm rolled out in September 2013 and was most notable because it was a major overhaul of Google’s core algorithm.
Google Maps
A service provided by Google that allows users to use roap maps, GPS-based route planning, Street View, and satellite layer imagery. Local businesses can increase their site traffic and brand visibility by appearing on Google Maps through the creation of a Google Business Profile Account.
Google My Business
Also Known As: Google Business Profile
A free service provided by Google to business owners which allows businesses to create profile that appear in local search results and in Google Maps.
Google Pigeon
A Google algorithm update designed to replicate Google’s primary web algorithm for local searches. This update was rolled out in 2014.
Google Pirate
An algorithm update from 2012 designed to reduce illegal piracy by promoting legal alternatives.
Google Possum
An unconfirmed Google algorithm update from 2016 that many suggest changed the way local search results were promoted in order to diversify the businesses that appeared.
Google Quality Guidelines
The published guidelines Google makes available. They outline and describe how Google rates web pages in order to provide the best search results for users.
Google Quality Raters
Googlebots that are distributed across websites globally in order to obtain information that will improve search results and better categorize information.
Google RankBrain
An AI based Google algorithm, connected to Google’s core algorithm which uses machine learning to learn from search data and internet signals in order to improve search results.
Google Search
The proper name for Google’s search engine.
Google Search Operators
Also Known As: Advanced Operators, Refine Web Searches
Special characters and commands used to make searching easier for searchers to obtain more specific results. For example, using quotation marks around search terms will results in pages that only have that exact terms that are within the quotes.
Google Sitelinks
The links below primary search results in Google’s SERPs that link to specific pages within a website.
Google Updates
A term that refers to a change in how Google ranks search results. The most common updates are algorithm changes.
Google's Mobile Friendly Update
A 2015 Google ranking change that boosted mobile-friendly website in the SERPs.
Google+
A social network developed by Google. The personal version of this platform was shut down in 2019.
Googlewashing
Homepage
The top page of a website. This is the page that is displayed when the domain is entered without additional URL path text. Your homepage is integral to on-site search engine optimization because the homepage is a doorway page for many consumers and site crawlers.
Hyperlink
A hyperlink is a link from one internet location to another. These links are activated by clicking on the highlighted word or phrase (anchor text) on the screen. Hyperlinking is the primary method used to navigate between specific pages and websites. Backlinks are a type of hyperlink that connects one website to another.
Information Architecture (IA)
Information architecture is the organization and structuration of content. The goal of information architecture is to help users find and use information seamlessly and sustainably. Information architecture is implemented in nearly every aspect of SEO. Identifying word choice for your content strategy and developing a quality responsive design require a strong knowledge of information architecture principles.
Informational Queries
A category of user search intent where the users want to gain information or learn about the topic they searched. For example: If a person Googles “weather patterns in Minnesota,” they’re likely wanting to learn about the weather in Minnesota–not buy something or find a particular website.
International SEO
Improving a website’s organic traffic through optimization in more than one country (or language).
Landing Page
A landing page is any web page on which a user may “land.” Concerning SEO, it is usually a standalone web page that consumers are redirected to after clicking a search engine link, hyperlinked email or advertisement.
Link
See Hyperlink.
Local 3-Pack
Related Terms: Local Pack, Map Pack.
The local three business or location results which appear beneath a preview map at the top of Google’s first page search results page.

Local Inquiries
A search for nearby businesses, organizations, and other locations.
Local Pack
See Local 3-Pack, Map Pack.
Local Search
An internet search with the intent of finding geographically relevant results.
Local SEO
Strategically optimizing a website in order to boost the site in Google’s local search results.
Map Pack
See Local 3-Pack, Local Pack.
Natural Language Processing
Also Known As: NLP.
AI that is programmed to understand human languages, both written and spoken.
Negative SEO
Related Terms: Negative SEO Attack.
Taking steps to lower a competitor’s search engine ranking unethically. This can include irrelevant and poor quality back linking and even hacking to change content.
Negative SEO Attack
See Negative SEO.
On-Page SEO
On-page SEO is optimized content that lives on your website permanently. Optimizing individual webpages on your site can help boost a site’s relevant organic traffic. On-page SEO flags your site for relevancy during the crawling process by using specific keywords. This includes content, meta tags, and URL paths.
Online Reputation Management
Reputation management plays a significant role in search engine optimization. When viewed online, it i strategically taking actions to gain or maintain control over the public perception of a business or brand. Online reputation management typically requires vigorous responses to review, social media marketing, and dynamic content creation.
Onsite SEO
See On-Page SEO.
Organic Ranking
Appearing in Google’s SERPs without the need of a Google Ads campaign.
Organic Search Results
Search results that naturally appear in response to a search query. Organic rank is in contrary to paid results, such as those that appear as Google Ads.
Organic Traffic
Web traffic that arrives on a web page after a link to the page appears in a search engine’s results for a search query. Organic traffic is contrary to direct traffic or paid traffic (often traffic through Google Ads).
Orphan Page
A web pages that is not linked to from any other page on a website. Orphan pages cannot be navigated to from internal links. They can only be accessed through direct links. Because there is no internal link to an orphan page, webcrawlers do not index them. The result is that orphan pages are excluded from SERPs.
Over-Optimization
Going beyond a normal level of SEO to the point where search engines begin to downgrade your rankings. However, if you follow SEO best practices, this should not be an issue.
Paid Search Engine Results
Web pages that appear for a search query because the site owner paid for advertising. These are in contrast to organic search results which appear based on keywords, domain rating, and other ranking factors.
Paid Traffic
The number of web visitors that arrive on a website through paid ads in search results.
Penguin
Penguin is a part of Google’s core algorithm. It is best defined as one of Google’s methods of rewarding high-quality sites and penalizing low-quality content. Penguin typically only negatively impacts sites that have engaged in black hat SEO.
People Also Ask
Questions related to search query terms.
Poison Words
Also Known As: Forbidden Words, Filter Words.
Words that have been identified as having a negative effect on a page’s ranking, should they be found in the page’s title, headings, meta description, or URL path. These can be words linked to actions search engines do not support (buying backlinks) or vulgar or politically incorrect terms.
Portal Page
Also Known As: Web Portal.
A web page that users usually sign into to view, edit, and input personalized information. Two of the most common types of portals a patient portal for a medical office or student portal. In regards to SEO, portals present a unique issues that they often lack enough content to organically rank.
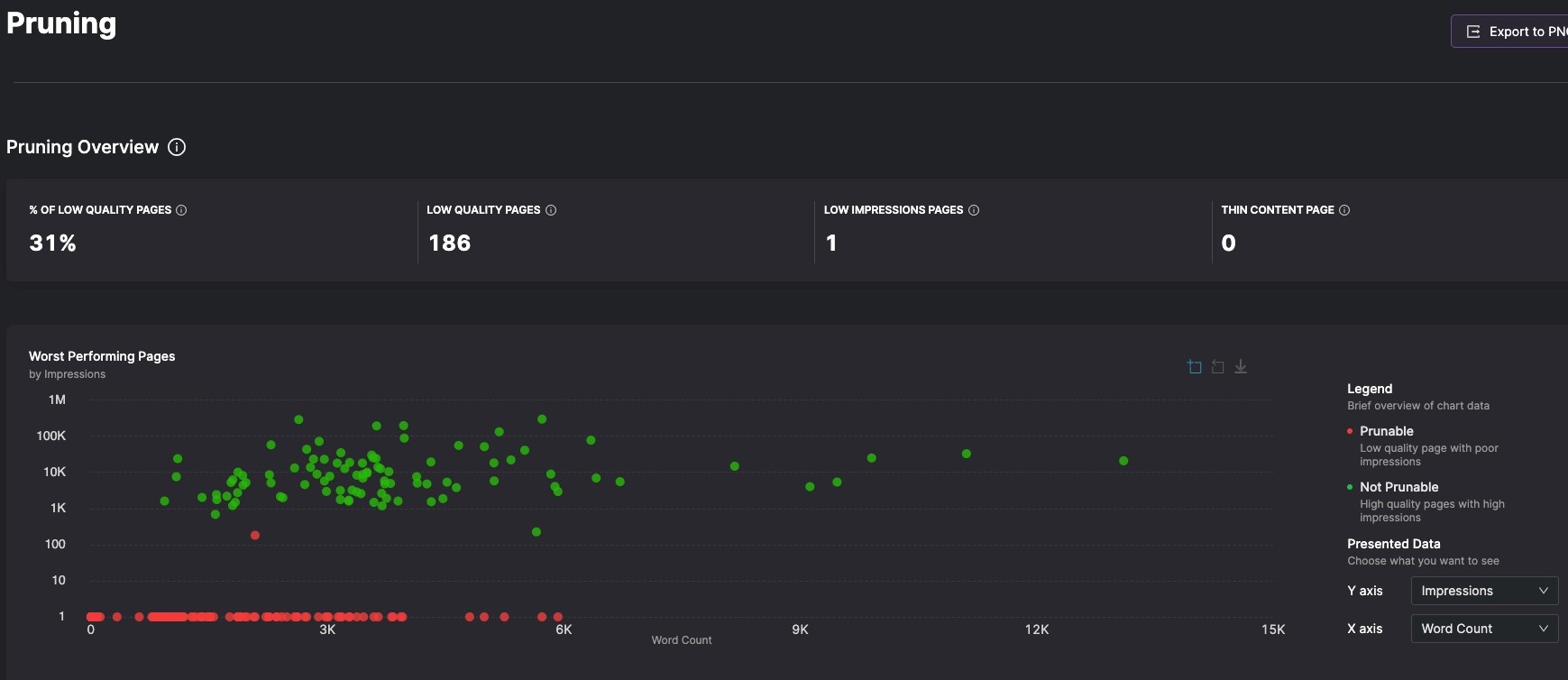
Pruning
Removing web pages from a website that do not perform well in order to reduce the number of pages Google indexes to improve the overall quality of a website.
Qualified Traffic
Visitors that arrive on your website who have a pre-existing interest in your website or offering. Visitors included in qualified traffic have a higher likelihood of making a purchase or another conversion.
Query
A query is a question usually intended to verify validity or accuracy. A user’s query refers to an internet user’s request to a search engine. Concerning digital marketing, any Google search bar request is a query for all intents and purposes.
Query Deserves Diversity (QDD)
An algorithm used by search engines (like Google) to pull and display a wider variety of search results in response to a search query that could benefit from a broader spectrum of web pages. The purpose of a QDD is to provide high quality results when a search engine is unsure of the user’s intent and to record how searchers interact with search results in order to learn what the searcher’s intent was and improve search results for the same query terms in the future.
Query Deserves Freshness (QDF)
An algorithm Google and other search engines uses to re-rank results based on how up-to-date the content is. This algorithm’s purpose is to provide users with the most recent information when temporality is important. These often include blogs, product reviews, news portals, and weather.
Ranking Factor
Ranking factors comprise of everything Google’s algorithm uses to determine a site’s placement on the search engine results page. Domain rating, topical depth, and page performance are all search engine ranking factors.
Rendering
Transforming website code into the website interface that visitor’s view and interact with.
Rep Management
Proactively and actively responding to how the public views and talks about a brand. This can include responding to reviews and engaging with social media users.
Return on Investment
Related Terms: ROI.
The amount of profit gained from a specific investment.
ROI
See Return on Investment.
Scraped Content
Information or content that is downloaded by a bot, often used on another website without permission.
Scraping
See Data Scraping, Web Scraping.
Scrum Board
A visual board indicating where you are in the process of completing a project or work sprint. Kabahn and Asana are two popular digital workflow platforms that use scrum boards to assist users in managing their workflows.
Search Engine
A software system that is designed to help web users to find information they’re looking for easily.
Search Engine Advertising
A paid promotional system that displays websites in web searches in response to specific search queries. Google Ads is the most popular search engine advertising platform. Many of these advertising systems use pay-per-click pricing systems.
Search Engine Algorithm
A complex digital system that finds and ranks web pages for search queries based on criteria with the goal of displaying the most relevant and valuable web pages based on the user’s intent.
Search Engine Bomb
See Googlebombing, Googlewashing.
Search Engine Marketing
Using paid ad campaigns and SEO to increase search visibility and traffic to a website.
Search Engine Optimization
Strategically refining a website and web pages to improve ranking in search engine results.
Search Engine Poisoning
Also Known As: SEO Poisoning.
An unethical attack strategy that uses web page creation with keyword packing in order to throw off a search engine’s ability to fairly rank web pages.
Search Engine Rank
The position a URL fills in the SERPs.
Search Engine Result Page (SERP)
The search engine results page is the location a search engine brings users to present them with websites and content it believes to be relevant to their query. All search results reside on the search result page.
Search Engine Spam
Tactics used to unfaily manipulate how search engines rank a specific or many websites.
Search Forms
Also Known As: Search Box, Search Bar.
The graphical element in websites, computers, and mobile devices where users can input a search query.
Search Intent
See Intent, User Intent.
Search Term
The text entered into the search box.
SEO Agency
A business that specializes in assisting website owners with improving their search engine visibility.
SEO Audit
Analyzing a website for the best practices for search engine ranking. This often includes looking at content, UX/UI, and web development elements.
SEO Service
A business that employs specific techniques and actions that will improve a website’s search engine ranking.
SERP Feature
A SERP feature is anything on the SERP that does not fall into the category of an organic result. Rich snippets and paid advertising methods like Google Adwords are SERP features.
Silo Web Structure
A website’s architectural structure that funnels visitors down a specific track, often from a more general topic to a more specific blog.
Site Audit
See SEO Audit.
Sitelink Extensions
A hyperlink to a specific page on a website. In Google Ads, a site link allows searches to land on a specific web page where they will find the information, product, or what it is they’re looking for.
The Fold
Related Terms: Above the Fold, Below the Fold.
The line that separates what is visible to web visitors before and after scrolling down.
Thumbnails
A small/compressed preview of an image, written content, or video.
Top Heavy
See Top Heavy Algorithm.
Top Heavy Algorithm
Related Terms: Top Heavy.
A Google algorithm that downgrades web pages with too many ads at the top of their pages or the ads so abundant, they disrupt the usability and usefulness of the page.
Traffic
The number of people that visit a website.
Transactional Queries
A search query that suggests the user would like to make a purchase.
Uniform Resource Locator (URL)
A unique address that locates a specific resource from the internet.
Universal Search
The ability for Google to take multiple forms of data and display them on the results page.

URL
URL or uniform resource locator is the specific web address of a given resource on the web. URL is the mechanism web browsers use to retrieve published resources like HTML pages, CSS documents, and more.
User Intent
Related Terms: Search Intent.
The meaning or driving force of a search engine query is the user intent. Google and other search engine’s primary goal is to satisfy it. The ranking factors and algorithms that dictate SERP placements are designed with the searcher’s intent in mind.
Vertical Search Engine
A software that performs searches within a specific set of web pages or content pieces. For example, Amazon, YouTube, and Pinterest are vertical search engines.
Visit
When a user is on a website.
Web Address
The unique URL that accesses a specific resource from the internet via a server.
Webpage
A file composed of hypertext on the World Wide Web.
Website
A collection of web pages under one domain name.
Website Architecture
The structural design of a website.
Website Traffic
The volume of website visitors your site hosts is your website traffic. The amount of website traffic you acquires directly affects lead generation, a driving factor in search engine optimization efforts.
White Hat SEO
In stark contrast to black hat SEO, white hat SEO is any technique used to build brand awareness, boost domain authority, and enhance overall website traffic that does not negatively manipulate search engine result rankings. Google’s algorithm updates are typically meant to reward white hat SEO and discourage black hat SEO. Any optimization efforts that provide users with a valuable piece of content can be considered white hat.
Intent
See Search Intent, User Intent.
Off-Page SEO
Related Terms: Offsite SEO.
Strategic activities outside of your website that boost your search rankings. This can include guest posting and infographic syndication.
Offsite SEO
See Offsite SEO.
Anchor Text
Anchor text is the clickable text that transports users to another internet destination. The hyperlink attached to anchor text may bring users to another URL or another website entirely. Google and other major search engines use anchor text as a way to understand what the linked URL’s content subject is.
![]()
Brand Keyword
Words or phrases directly associated with a specific business, organization, or group of businesses. For example, the Big Mac is keyword that is almost exclusively associated with McDonald’s.
Citation
Also Known As: Local Citation.
The mention of a business by its name, address, and phone number. Citations may be used by search engines to verify a business’s legitimacy and are likely a ranking factor.
Content Management System (CMS)
Also Known As: CMS.
Software that allows and helps users add, manage, and edit web content without the need to use to code. WordPress is an example of a CMS.
Content Marketing
A marketing strategy that uses the creation of valuable, interesting, unique, and relevant content to build brand following and retain users.
Content Silo
A grouping system for content that establishes a website’s topical areas, often based on keywords.
Cornerstone Content
Also Known As: Flagship Content.
The most important, foundational content on your website. This is the most used content of a website, often the reason why people visit a website.
Duplicate Content
Text that appears on the internet in more than one location.
Email Outreach
Emailing content or promotional content on products to a select list of people with personalized messages.
Exact Match Anchor Text
Anchor text, or linked text that contains the keyword that page being linked to is trying to rank for or ranking for.
Freshness
Updated or new web content. Google uses freshness as a ranking factor when newer information produces better results for what searcher is attempting to find or learn. For example, a sports team’s schedule that has been updated to reflect upcoming events provides more value than a schedule from the previous year.
Gated Content
Content that is not available openly to users unless they pay or enter their information. Gated content will not appear in Google searches.
Guest Blogging
Related Terms: Guest Posting.
Sometimes, guest blogging is referred to as guest posting. Guest blogging is a form of content marketing that involves writing and publishing blog posts on other websites’ blogs within your industry. This common SEO tactic is beneficial for gaining referral traffic and boosting domain authority. Additionally, it can help your business build relationships with other industry professionals.
Guest Posting
Related Terms: Guest Blogging.
An approach to link building where you or someone from your website contributes a blog, quote, or article to another website and receive a link to your website in return.
Guestographic
Similar to guest posting, however, instead of offering another website a blog, you offer them an infographic they can post in exchange to a link to your site in return.
Heading Keyword
A keyword that should appear in one of your headings.
Image Carousel
A slideshow of images that a user can scroll through left-to-right or vice versa. They can also be automated to shift images at set time intervals. Image carousels can be used on website or social media platforms.

Image SEO
The process of optimizing images on a website in order to make them more easily discoverable by search engine webcrawlers. Image SEO can improve a website’s ranking, especially when it comes to image searches.
Keyword Analysis
Strategically looking at keyword metrics to better understand and plan for organic and paid search campaigns.
Keyword Cannibalization
When multiple pages on a website rank for the same or similar keywords. This confuses Google as to which page should appear. Sometimes one or both pages will be hidden or demoted in the SERPs because of this confusion.
Keyword Categorization
Organizing your keywords by commonalities to better construct keyword pillars and clusters.
Keyword Competition
See Keyword Difficulty.
Keyword Density
How often a keyword occurs compared to other language in a webpage.
Keyword Difficulty
Related Terms: Keyword Competition.
How easy or difficulty it would be to rank for a specific keyword.
Keyword Optimization
Researching, analyzing, and implementing keywords in a website’s content in order to drive more traffic from search engines to the site.
Keyword Proximity
How nearby keywords from one search query appear in relation to one another. The closer the words, the more relevant to the searcher through the eye of the search engine. For example, if someone searches “veterinarian Nashville” and Google looks over existing pages and finds “Experienced Small Mammal Veterinarian in Nashville,” the proximity of the keywords is one word (in).
Keyword Research
Identifying and analyzing keywords in order to improve a website’s search visibility.
Keyword Spam
See Keyword Stuffing.
Keyword Stemming
Using an existing keyword as the foundation to build related words by adding prefixes and suffixes before and after the existing keyword or changing the word form. For example, landscape stems to landscaper, landscaping, landscapes.
Keyword Stuffing
Keyword stuffing is a black hat tactic. It involves taking as many keywords related to your products or services as possible and unnaturally forcing them into your content. Keyword stuffing is harmful to your user experience because it makes your webpage crowded and difficult to understand. Additionally, keyword stuffing may be flagged by Google’s algorithm, earning penalizations.
Keywords
Keywords are defined as phrases, words, or topics that describe your content. In SEO terms, keywords are the specific contents of the queries that searchers enter into search engines. Google and other major search engines use keywords to identify relevancy and similar content.
Long-Tail Keyword
Long-tail keywords make up the majority of search engine queries. They are multi-word, specific keyword phrases that website users enter into the search bar. Smaller companies and niche industry businesses can benefit greatly from optimizing for long-tail keywords.
LSI Keyword
Also Known As: Latent Semantic Indexing Keywords.
Keywords that are topically related to the primary keyword. For example, if a searcher were to Google “salon,” some LSI keywords may be hairdresser, facial, spa, manicure, pedicure, and hair stylist.
Main Keyword
The primary keyword that an article, landing page, or any other web page is targeting.
Outreach Marketing
Contacting and pitching to organizations outside your own that may have an interest in your offering.
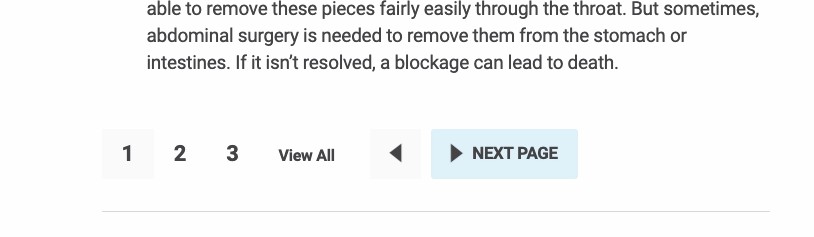
Pagination
Dividing large pieces of content into multiple pages, most commonly guides and blog articles on longer topics. This can improve a search engine’s ability to direct searchers to the specific information they’re seeking.
Primary Keyword
The words or phrases that a website wants to rank for.
Resource Pages
Also Known As: Pillar Page.
A reference page that provides valuable information with a more macro approach to the topic with links to related pages. Often keyword clusters are built around the topic covered in the reference or pillar page.
Secondary Keywords
Words and phrases that are related to the primary keyword that searches may also use to find a web page.
Seed Keywords
Short-tail keywords (1 or 2 words). These keywords often have extremely high search volume as well as competition.
SEO Silo
Dividing content topics into groups or sections in order to bolster and improve the website’s topical depth, keyword variety, and navigability.
Stop Words
Common words that search engine’s NLP’s filter out since they often do not add very much meaning to the phrase. Often, stop words include articles (a, an, the) and prepositions such as “in.”
Target Audience
Being able to identify and understand your niche is essential to any digital marketing strategy. Your target audience is the group of consumers or demographics that you aim your marketing efforts towards.
Term Frequency
See Keyword Frequency.
User-Generated Content
Written material, images, or video created by people that post to a website or web page.
Video Optimization
Strategically formatting a video and its related web elements to make it optimal for webcrawlers to assess and search engines to find.
Backlink Profile
A backlink profile is a website’s collection of backlinks. When analyzing a backlink profile for quality, consider the following insights:
- Total number of links acquired
- Usage of anchor text
- The quality of each backlink
- Page performance
Backlinks
A backlink connects a 3rd party website to another website. High-quality backlinks are essential for building brand awareness and increasing a website’s search engine rank. Backlinks are also referred to as incoming links or inbound links (when linked to your website) because they make an incoming connection from external websites.
Directory Links
Links that originate from a web directory, or collection of website links that have been categorize to help users locate websites that fit within a subject matter. Some people submit their websites to directory as a way to build backlinks.
Disavow Links
These links are created using the Google disavow tool. They are used to notify Google of poor-quality links directing users to your website that you do not want associated with your website. Using disavow links gives you power over which referral links Google should count in its ranking factors for your website.
Dofollow Link
Links that allow search engines to point back to your website. Dofollow links can increase your domain rating if the linka come from a quality site.
Domain Rating (DR)
A metric used by Search Atlas that predicts a site’s probability of appearing in Google’s SERPs based on the quality and number of backlinks.
Editorial Link
A link from a high-quality third-party website that was not paid for.
Inbound Link
An inbound link or internal link is a link that transports people from another website to your website. A backlink is referred to as an inbound link by the person on the receiving end of the link. Inbound links are one of the most important ranking factors that search engines use to determine your credibility as a site.
Link Acquisition
See Link Building.
Link Building
Link building is the search engine optimization strategy of acquiring links. Digital marketers and site owners value link building with other sites that have high domain authority because it drives referral traffic from relevant websites and boosts domain authority scores.
Link Buying
An artificial form of link building in which the linked-to website pays for links in order to boost their domain rating.
Link Farm
A website or group of websites that link to other website strictly for the purpose of link building and artificially inflating the linked-to websites’ domain rating.
Link Reclamation
Updating, replacing, fixing or removing broken referral links to a website.
Link Value
Also Known As: Link Juice.
The equity passed through a hyperlink from one webpage or site based on the referral link’s domain rating.
Organic Links
Also Known As: Natural Links.
Hyperlinks that link to an external website without an agreement between the sites for the link. This is contrary to link exchanging or purchased links.
Outbound Link
Related Terms: Outgoing Link, External Link.
Outbound links are also known as external links. They are the polar opposite of backlinks. An outbound link directs users from your blog post or website to an external site.
Outgoing Link
See Outbound Link, External Link.
Paid Links
Backlinks that have been purchased by the website being linked to. The purpose of paid links is to improve a website’s domain rating.
Purchased Links
See Paid Links.
Reciprocal Linking
Working with another website and linking to one another for the mutual benefit of link equity.
Referral Traffic
This term refers to any traffic that your site receives from other sources. Publishing a blog post on another website’s blog is seen as a vote of confidence, promoting website traffic.
Short-Tail Keywords
Search query terms that are only one or two words long. These are often highly competitive since they have high search volumes, and they are also more generalized.
Spider
See Crawler, Web Crawler.
SSL Certificate
A digital certificate that demonstrates that a website is authentic/verified and encrypts its data transferred between the server and user.
Static Link
Also Known As: Static URL.
A hyperlink that copies all library modules into the a final file. Static links differ from dynamic links in that the URL path never changes. A dynamic link is produced at the time of a user’s request.
Static URL
See Static Link.
Syndicated Content
See Content Syndication.
Technical SEO
The digital side of search engine optimization techniques, that often deal with website development and preparing a website for optimal crawlability. This can include:
- Rendering
- Mobile-Friendliness
- SSL
- Indexation
- Crawling
- Page Migration
- Site Structure
- Keyword Research
- Content Optimization
Unnatural Link
A link that does not relate to the linked web page’s content or topic.
Technical Aspects of SEO
This section will help you learn the basics of programming language in relation to SEO, SERP features, and common technical SEO terminology.
H1
An H1 is an HTML heading that appears like a headline to searchers. It is used most commonly to mark up a web page title. Simply put, an H1 tag is the page title. For SEO efforts, it can be highly beneficial to use your top keyword in creating an H1. H1s are one of the ranking factors that Google considers when determining a webpage’s relevancy to a specific keyword or search query.
Heading Elements
See H1-H6 Tags, Header Tags.
Mobile Optimization
Formatting and revising a web page or website to make it easier for people to view and use on mobile devices such as smartphones and tablets.
Mobile-First Indexing
When webcrawlers index a page, they will index the mobile version before the desktop version.
Mobile-Friendly Website
Websites that are formatted and optimized to perform better on smartphones and tablets.
Rich Snippet
Also Known As: Rich Results.
A results page snippet that display more information than just the typical meta title, description, and URL path.
Meta Description
A meta description is a short description that appears under a the meta title (or hyperlinked text) on the search engine results page. It is best described as a summary of the webpage’s content. Meta descriptions should be appropriately keyword-optimized without compromising natural readability.

Meta Description Tag
See Meta Description.
Meta Keywords
A type of meta tag that appears in a web page’s HTML to assist search engine webcrawlers to better understand the topic of the page’s content.
Page Title
HTML code that displays the primary heading of a web page in search results.
Title Tag
A title tag is an HTML tag that names your web page. It is shown in the browser’s title bar and on the SERP. Optimizing title tags are essential for boosting your organic search engine rankings.
301
Also Known As: Redirect 301, 301 Redirect, HTTP 301.
This is a server response code from the server, indicating the page has been permanently moved the new URL. The command to the server to redirect the user to the new webpage/URL.
302
Also Known As: Redirect 302, 302 Redirect, HTTP 302.
A server response code indicating the page has been temporarily moved/redirected to a new URL.
404
Also Known As: Error 404, HTTP 404, 404 not found, 404 code.
A response code that means the server cannot locate the URL/webpage. This is often because the page has been removed from the website. This is also referred to as a “dead link” or “broken link.
2xx Status Codes
The request sent to the server was successful, and the browser can load the webpage.
4xx Status Codes
The 4XX server codes mean there has been an error on the server side when it comes to retrieving the webpage, and the URL cannot be reached.
Absolute Link
A hyperlink that contains the full URL, including the protocol (HTTP or FTP), domain name, directory or subdirectory, and file name if applicable (such as HTML, PDF).
![]()
Accelerated Mobile Pages (AMP)
A tool within Google Ads designed to help mobile pages load faster. The goal of this tool is to lower abandonment rates and bounce rates while increasing conversions.
Alt Attribute
HTML that is designated to elements that load should the element not be rendered. Image alt texts are one example. If the image cannot load, the alt text displays so the viewer understands what should have been displayed.
ALT Text
Alternative or ALT text is the short description applied to image tags that provide context to search engines and visually impaired users about what the image is depicting. ALT text is an HTML attribute, also sometimes referred to as an ALT tag or ALT attribute. ALT text is vital to SEO because it can be optimized to include keywords or indicate topical relevance to webcrawlers.
![]()
Bots
Related Terms: Googlebot, Webcrawler, Spider.
A bot is also sometimes referred to as a Googlebot, web crawler, or spider. A bot is the web crawling software Google and other search engines use to collect information for its indexing system that is used in its ability to provide search results. Bots search the web and analyze websites to support SERP ranking efforts. Bots crawl your site to provide Google’s algorithms with important ranking factor data.
Broken Link
Also Known As: Dead Link.
A broken link, sometimes referred to as a dead link, is a link that is no longer usable. Often, after clicking a broken or dead link, you will be redirected to a dead-end page displaying an error message. In SEO, some people seek out broken links on websites. Reaching out to a webmaster to replace a dead link on their website with a link to your website enhances your backlink profile and improves their website’s user experience as well.
Canonical Tag
Also Known As: rel=”canonical”.
HTML that tells a search engine that the page is the master copy of content that is duplicated elsewhere on the internet. The purpose is to prevent SEO issues related to duplicate content, such as syndicated content.
Canonical URL
A canonical URL is an HTML element. It helps webmasters identify and solve duplicate content issues. As an SEO term, “canonical URL” can be regarded as the preferred presentation of a webpage.
Channel, Marketing
A group of people, organizations, activities that results in a product going from production to ownership.
Crawl
See Web Crawlers, Spider, Spider Bot.
Crawl Depth
The extent to which a search engine is able to index a page using its bots (or crawlers).
Crawl Rate
The number of requests per second a Googlebot initiates when crawling a website. You can change your website’s crawl rate to slow down the Googlebots, so they do not bog down your server, however, this will result in a shallower crawl.
Crawl Rate Limit
See Crawl Rate.
Crawler
See Web Crawler, Bot, Spider.
Crawler Directives
The instructions or directives given to a crawler to tell them how to behave when indexing a website. These include robot meta tags and x-robots tag.
Crawling
When a bot ‘reads’ a website in order to gather information and index it to improve and update search engine results.
CSS
Also Known As: Cascading style sheets.
A language used for how elements are displayed on a web page. CSS allows web elements to scale according to the size of the screen or type o device.
De-Indexing
Having your website removed from appearing in search engine results. Webcrawlers will skip a deindexed site. This technique can be a way to prevent issues related to duplicate content, hide outdated pages you want to update in the future, or hide gated content.
Dead Page
See Dead Link.
Dead-End Page
A page that has no internal links on it. The user reached a dead end in their journey through the website should they be clicking on internal links. If a webcrawler reaches a dead end, it will stop indexing the page.
Deindexed
A website that has been removed from a search engine’s index, so that it does not get crawled.
Error 404
See 404.
Geographical Modifiers
Also Known As: Geographical Keyword Modifier.
The addition of a word that specifies the location for which searcher wants to limit their search results. For example, if a searcher were to Google “dog training Nashville,” “Nashville” would be the geographical modifier.
Google Webmaster Guidelines
The guidance provided by Google to webmasters on how they can best optimize their websites to be found by Google.
Googlebot
Related Terms: Bot, Crawler, Spider, Web Crawler.
A web crawler that Google uses to go through the web and replicate the actions of desktop users and mobile users while recording data.
HTML
HyperText Markup Language, or HTML, is a basic scripting language. Web browsers use it to render pages on the internet. This scripting language is regarded as the standard markup language used to create web pages. In other words, HTML is the code used to develop site structure and a web page’s content.
HTML Sitemap
A list or table of contents that includes every page on a website. These ‘maps’ make navigating a website easier. HTML sitemaps are most often used by web users, versus XML sitemaps, which are mostly used by webcrawlers.
HTML Source Code
The foundation of how a website should look through the use of HTML (a markup language).
Indexability
See Crawlability.
Indexing
The process of organizing information about and from websites that search engine crawlers gather to improve search engine results. Google uses indexing to analyze written content, images, videos, and more.
Internal Link
A hyperlink from one page on a website to another within the same website.
Jump Page
A webpage used to redirect visitors to another page.
Lazy Loading
A web design or web development pattern in which the content on a page doesn’t load until the user arrives at it. The purpose is to optimize load time for the content the user would view or interactive with first. For example, images below the fold may not load at the initial loading of the page. It will load once the user scrolls down.
Local Business Schema
Structured markup code that is added to a business website to more easily signify to Google’s webcrawlers of the type of website in order to be more easily discoverable.
Meta Redirect
Meta Refresh Redirect
Also Known As: Meta Redirect, Meta Refresh Tag.
When a user is automatically transferred from one web page to another after a set amount of time, often 2 to 3 seconds.
Meta Refresh Tag
Metadata
See Meta Tags, Meta Robots Tag.
Nofollow Link
Also Known As: No Follow Link.
An HTML tag that tells Google to not count outbound links towards the linked website’s ranking. The motivation for using a nofollow link would be to prevent spammy links that could lower the site’s domain rating.
NoIndex Tag
Also Known As: No Index Tag.
An HTML tag that tells webcrawlers to not crawl or index the website. A noindex website will not appear in search results. The motivation for using a noindex tag is to protect gated content or hide outdated material.
Redirect
Automatically navigating a browser user to a different web page.
Redirect 301
See 301.
Redirect 302
See 302.
Relative Link
Also Known As: Relative URL, Relative Path.
A form of HTML linking using href tags that does not use the domain in the path (unlike absolute links). Webcrawlers will automatically populate the full URL path, however, relative links often load faster than absolute links. For example: <a href=”/blog/SEO-basics.html”>Click Me</a>
Relative Path
See Relative Link, Relative URL.
Relative URL
See Relative Link, Relative Path.
Relevant Link
A hyperlink that is topically connected to or related to the linked-from web page.
Robots.txt
A file that tells search engine crawlers which pages they can access on a website.
Schema
A semantic language of HTML tags that categorize the information type or business type to help search engines find the web pages more easily. For example, you can use product schema to indicate a product’s brand, color, reviews, size, and model.
Schema.org
A database of schema markup to promote schema use, standardize schema markup, and make schema vocabularies available to everyone.
Search Engine Index
A set of data about webpages and content that Googlebots analyzes for meaning and then they are placed into categorizing system. The search engine index is then referenced when determining query relevancy.
Secure Hypertext Transfer Protocol
See HTTPs.
Site Structure
How a website’s pages are organized.
Site-Wide Link
A hyperlink that appears on every page of a website. This can be in the header, footer, sidebar, or elsewhere. the most common examples include About, the shopping cart, and Home.
Sitemap
A sitemap is a file where information about webpages and their contents are provided. Sitemaps also contain valuable information about the relationships between content. A sitemap lets Google know which pages and files are most important on your site and what needs to be known about them.
Submission
A request that your website be indexed by a search engine.
Web Scraping
See Scraping, Data Scraping.
Webmaster Guidelines
X-Robots-Tag
A HTML tag in the HTTP section of the header that directs webcrawlers how to index a page in its entirety and its individual elements.
XML Sitemap
(Extensible Markup Language) a text file that details all URLs on a website, including metadata for each URL. This file assists in how search engines will crawl the site.
PageRank
The system or algorithm of valuing webpages used by Google.
Algorithm Penalty
A demerit or negative signal that occurs when a webcrawler indexes a page. These penalties can add up to a lower SERP ranking.
Algorithm Update
When a search engine updates the algorithms that it uses to rank web pages in organic search results. Updates can be small changes or larger introductions of new algorithms. Often, major changes or grouped together and given a named. For example, Google’s Penguin update.
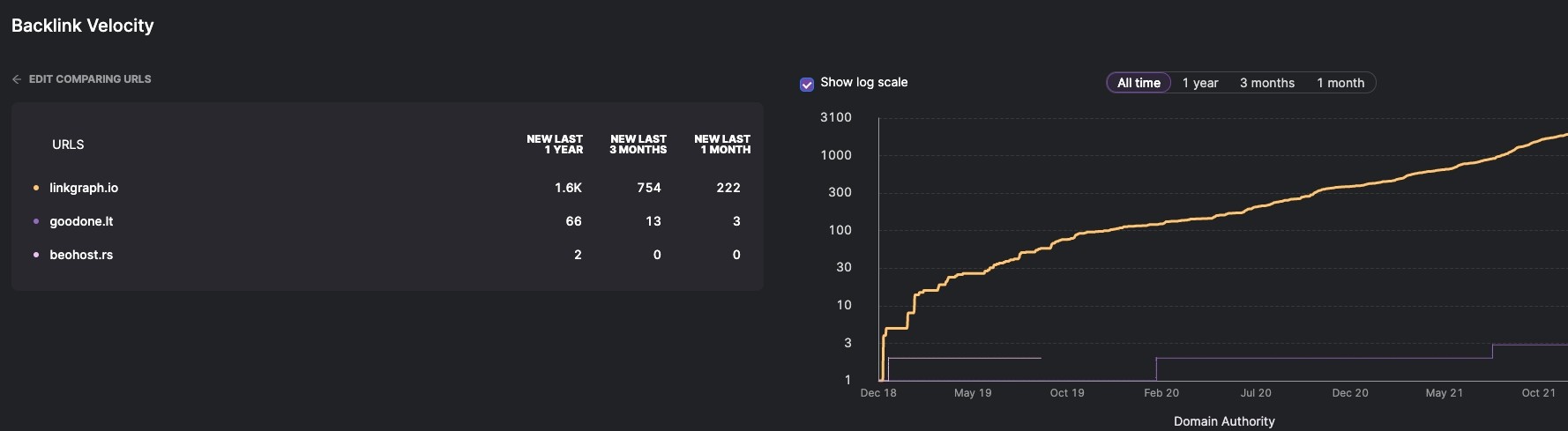
Backlink Velocity
A tool in the BackLink Analyzer that presents the trend of how many sites are linking to yours.
Black Hat SEO
Black-hat SEO practices refer to search engine manipulation. Google and other search engines’ primary goal is to satisfy user intent. Accordingly, any negative SEO actions that hinder the SERP ranking process can be categorized as black-hat SEO. SEO efforts must be backed by quality content that is relevant to industry queries. Sneaky SEO tactics like redirects, invisible text that capitalizes on specific keywords, or keyword stuffing are likely to become vulnerable to penalizations or de-indexing by Google’s algorithms.
Bounce Rate
The number or percentage of visitors who navigate onto a website from the SERPs then leave or back out. When this occurs, Google often views it as the user deciding the content was not relevant, the load time was too long, or the page experience was subpar. Google sees a high bounce rate as a negative ranking factor.
Click-Through Rate (CTR)
Also Known As: CTR, Click Through.
A click-through rate is an excellent metric for determining how well your keywords and ad strategy are performing. In paid search, CTR is the number of clicks your advertisement receives divided by the number of times your advertisement is shown. CTR also applies to organic search results. Click-through rate will be shown in Google Analytics as a percentage. For example, if your website garners 25 clicks out of 100 impressions, your CTR is 25%.
Conversion Rate
Like the CTR, Google Analytics will also give a website’s conversion rate as a percentage. Conversion rate is the percentage of website visitors that performed the desired action. A high conversion rate is telling of a successful marketing strategy and website design. Conversion rate is calculated by taking the ratio of defined actions to website visitors and multiplying it by 100.
Cost-Per-Acquisition (CPA)
See Pay-Per-Acquisition.
Cost-Per-Action
See Pay-Per-Action.
Cost-Per-Click (CPC)
Also Known As: Pay-Per-Click.
Often associated with Google Ads, this term refers to the amount you would pay each time a user clicks on your search engine ad. This model allows advertisers to pay for clicks rather than impressions.
Dwell Time
The length of time a user spends on a page after clicking onto it from the SERPs.
Economic Value of Traffic
An estimate for the total monetary value of the traffic a site is getting from organic search. Calculated as the keyword CPC traffic for each keyword your site organically ranks for.
Entry Page
The first page a searcher views on your website–the page they use to “enter” your site through.
Exact Match Keyword
A keyword setting within Google Ads that tells Google to display your ad should the designated keywords, verbatim, be searched.
Focus Terms
Words semantically related to a primary or target keyword. Including Focus Terms within your content can increase your Content Score, which reflects its potential to rank.
Google Keyword Planner
A tool within Google Ads that allows users to research keyword ideas or view search volume on pre-researched keywords.
Google Manual Action Penalty (MAP)
An action Google takes to demote or remove a web page or site from its results for spammy behavior. Users will receive a notification on their Google Search Console account regarding the reasoning.
Google Mobile-Friendly Test
A tool provided by Google that allows you to test the experience mobile users will have if they visit your web page.
Google PageSpeed Insights
A tool that allows users to enter a URL in order to view speed metrics, many of which are integral to a website’s ranking.
Google Penalty
Google Search Console
The Google Search Console is a free service offered by Google to website owners, admins, digital marketers, and web developers. The Google Search Console contains a dashboard of insights regarding keyword research, page performance, security risks, and more. GSC was designed to act as a central hub of website information that can be easily accessed and analyzed even by those with little to no technical SEO knowledge.
Google Trends
Google Trends is a tool that allows people to see what internet users worldwide are searching for. This dataset is anonymous, largely unfiltered, and consists of search requests to Google from actual users. Using Google Trends is the best practice for SEO strategists to track trending topics.
Google Webmaster Tools
GSC Insights
Search Atlas software that allows users to track web traffic from Google organic search results to their websites.
Impression
An impression is an indication that a user has seen your advertisement or link. For example, in the Google Search Console, you can review the number of times that any URL from your website has appeared in the search results and been viewed by a searcher. These are not indicative of clicks or actual site visitors.
Key Performance Indicators
Also Known As: KPIs.
Key performance indicators are quantifiable measurements used to evaluate the success of a marketing campaign. What are considered KPIs changes depending on the specific organization or project that they are measuring. KPIs can help indicate the progress or success of a strategy. Common key performance indicators used in SEO include conversions, bounce rates, and increases in keyword rankings.
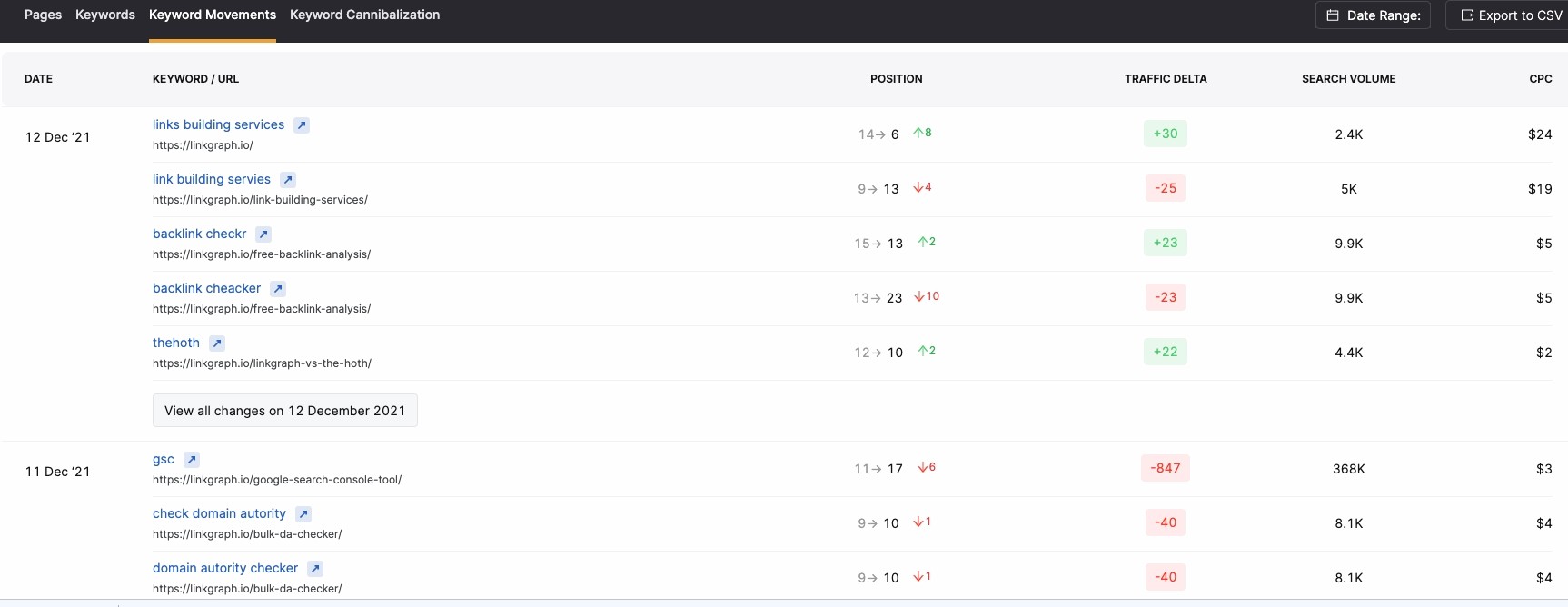
Keyword Movement
The position change of a website’s keyword ranking in the SERPs.
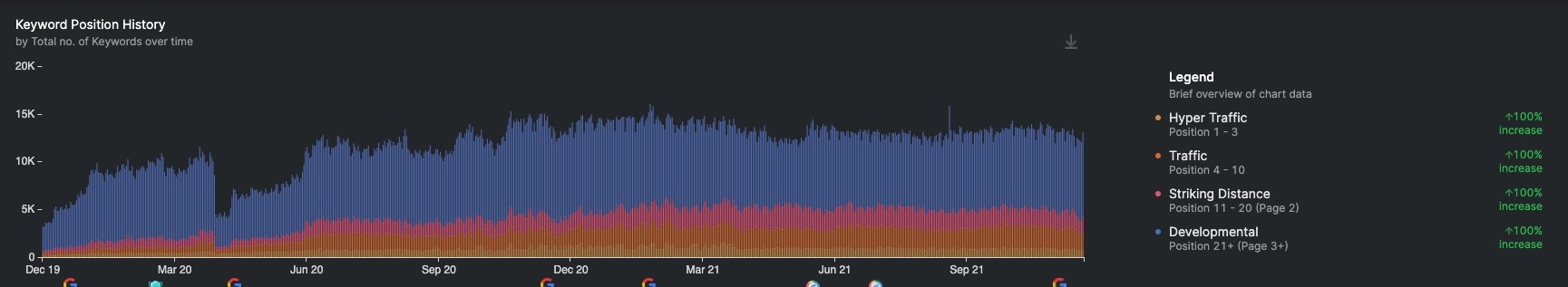
Keyword Position History
A graph tracking where all of a website’s pages appear in the SERPs for keywords the website ranks for.
Keyword Rank
The position of a webpage in the SERPs for a specific keyword.
Metric
A quantifiable measurement used for analysis or tracking.
Page Grouping
A Search Atlas tool that allows website owners to group their pages into categories in order to view how each group performs in the SERPs.
Page Impression
The number of times a page is seen by web searchers.
Page Rating
Also Known As: PR.
A score within Search Atlas that indicates how likely a web page is to rank within Google’s search results.
Pages Per Session
A metric within Google Analytics that measures the average number of web pages users visit for each visit.
Pageviews or Page Views
The number of times a web page is clicked onto and loaded by searchers.
Pay Per Acquisition
Also Known As: Cost Per Acquisition.
The total average cost of acquiring one paying customer.
Pay Per Action
Also Known As: Cost Per Action, PPA.
An online advertising pricing model where the advertiser pays for each defined action (click, form submission, etc.).
Readability
A metric that reflects how easy or difficult text is to understand. In Search Atlas’s SEO Content Assistant, you will find the Readability scale is a way to gauge how readable your content is compared to your competitors.
Scroll Depth
The distance a visitor scrolls down a web page. This metric is tracked in Google Analytics.
Search Traffic
The visitors to a website that arrive by clicking a search engine results link.
Search Visibility
A metric that represents the likelihood a searcher will see a website based on all of the website’s keyword rankings.
Search Volume
The estimated number of search engine inquiries for a specific search term.
Session
The actions and path a visitor took on a website without exiting the site.
Thin Content
Often seen as a penalty, this term refers to a website or web page that does not have substantial or adequate content/value to users, which is a red flag that the website may be spam or a scam.
Time Spent on Page
Related Terms: Time on Page.
Often confused with dwell time, this metric refers to how long any visitor stays on a web page, no matter how they arrived there. Dwell time measures the amount of time a user from the SERPs arrived on the page.
Time-On-Page
The amount of time a user is on a search result before clicking back to the search results.
Topical Relevance
Also Known As: Link Relevance.
How related the referral link’s website is to your own.
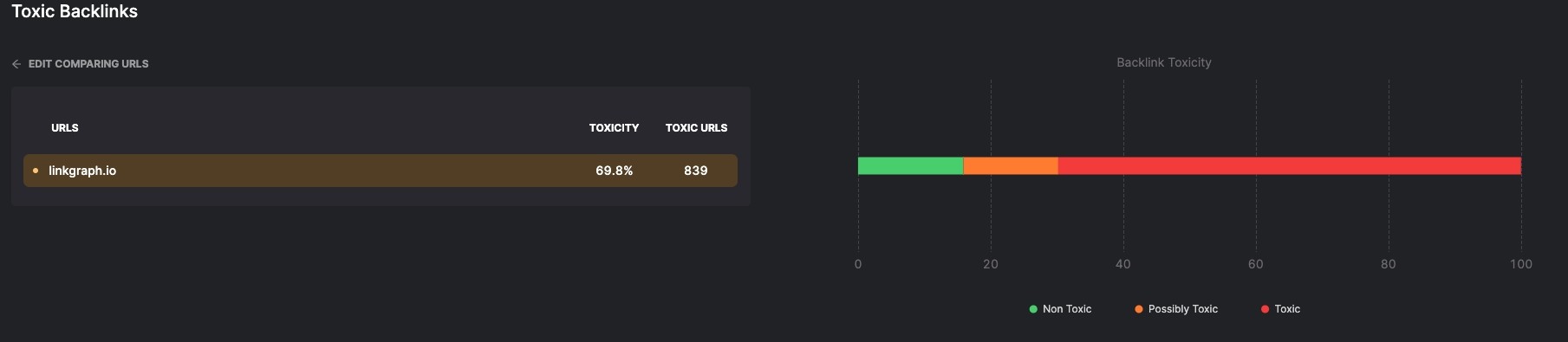
Toxic Backlinks
Links to your website from low authority sites that are often have a negative effect on your Domain Rating.
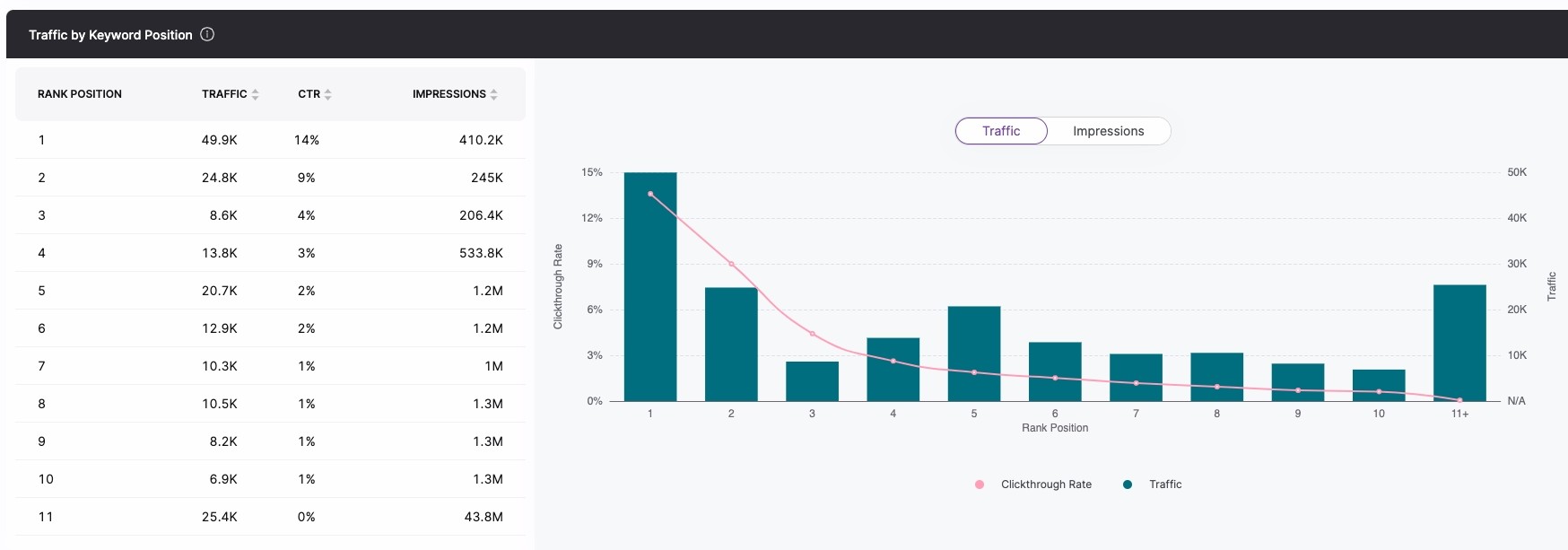
Traffic by Keyword Position
A chart with the Search Atlas SEO software that illustrates the total amount of traffic your site received from keywords by ranking position on Google.
Traffic Potential
An estimate of how many monthly organic search engine users will use a web page, website, or cluster of web pages.
Unique Visit
A metric that reflects how many individual users visit a web page or website, excluding any additional visits from a user that has already been on the page.
User Engagement
A measurement of how useful web visitors consider a product page or service page.
Page Experience Terms
Above the fold
Related Terms: The Fold, Below the Fold.
Anything visible on a webpage before the user scrolls down.
Below the Fold
Related Terms: The Fold, Above the Fold.
The section of the website that is not visible to the user before scrolling down.
File Compression
Shrinking the data within a file, such as an image, to save space or increase load time. Ideal file compression will retain the file quality for its designated purpose.
Google Core Web Vitals
A report connected to Google’s 2021 Page Experience Update that measures LCP, FID, and CLS.
HTTP
Also Known As: Hypertext Transfer Protocol.
An application layer protocol. This code allows a internet browser to communicate with a website in order to transfer and display informations. Unlike HTTPs, HTTP does not encrypt the information sent or input by the browser user, and is therefore less secure.
HTTP Response Status Codes
Categories of codes that servers send to web browser users to indicate the ability to fulfill or not fulfill the request and why. Status numbers are categorized: 1XX: Request received, 2XX: Success, 3XX: Redirection, 4XX: Client error, 5XX: Server error
HTTPs
Also Known As: Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure.
An application layer protocol that servers send to web browsers in response to the browser’s request. Unlike HTTP, HTTPs encrypts the user’s information and is more secure.
HTTPs Status
Page Load Time
The amount of time it takes a web page to display all elements.
Page Response Time
The amount of time it takes a server to respond to a given request.
Page Speed
Page speed is the measurement of how quickly the content on your webpage loads. Page speed for mobile devices should be up to par with desktop web server performance. Not to be confused with site speed, page speed refers to a webpage’s load time. Site speed is the page speed for a sample of page views across a website.
PageSpeed Insights
A free tool that tests websites and web page load time speeds. You can enter your URL into the search bar and receive reports regarding your mobile and desktop speeds for varying elements.
Responsive Design
Also Known As: Responsive Web Design.
An approach to designing a website and web pages that prioritizes a page’s ability to adjust to screen size, including orientation and how the user will interact with the web page.
Usability
Usability is the measurement of how well a website user can achieve their defined goal. Trademarks of a website with good usability are as follows: pleasant webpage design, rapid page speed, and responsive interactions.
User Experience (UX)
A website’s UX or user experience refers to the pleasantness (or unpleasantness) a user is exposed to when visiting your website. Response time, user interface, and information architecture design all play a significant role in user experience.
User Interface (UI)
The part of a website that people see, use, and interact with.
User-Friendly
A way to describe a web page or website that is intuitive for visitors.